-
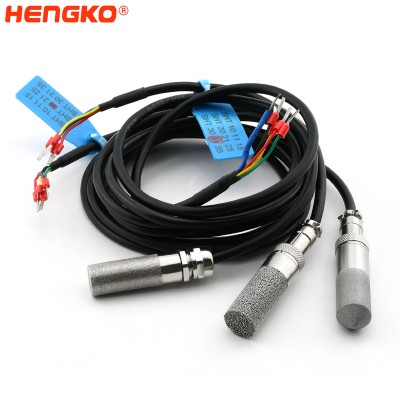

HENGKO IP67 waterproof exchangeable relative humidity and temperature sensor probe with...
HENGKO humidity sensor probe adopts high precision RHT-H serious sensor is a cable type sensor in the digital temperature and humidity sensor series. The sen...
View Detail -
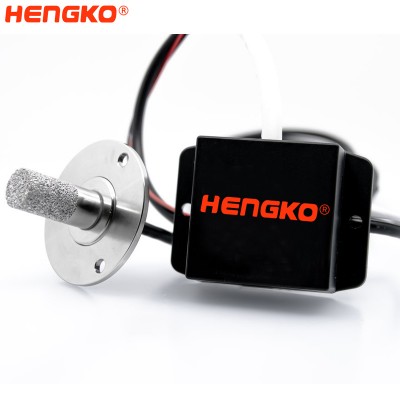

High precision wireless industrial I2C RHT-H serious high temperature and relative humi...
In high-altitude flight, the temperature and humidity sensor probe housing is an important protective tool to protect the chip from damage. It must have a ha...
View Detail -
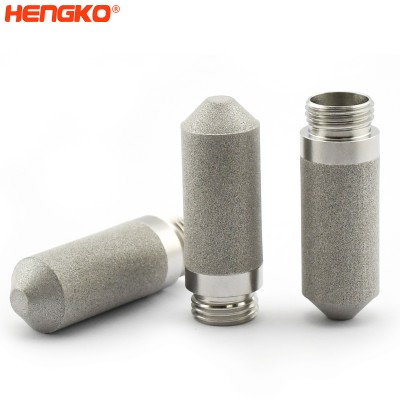

Anti-collision RHT-H30 Sintered SS316L temperature and humidity sensor probe housing HK...
HENGKO temperature and humidity housing adopts high precision RHT series sensor equipped with a sintered metal filter shell for large air permeability, fast ...
View Detail -
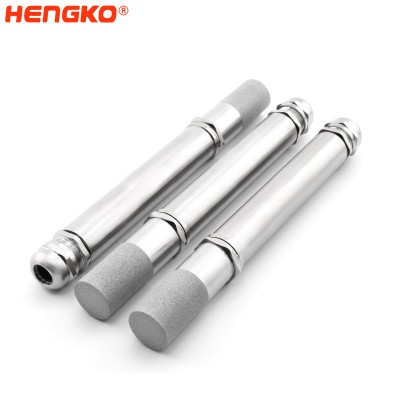

Stainless Steel Probe Filter Housing Temperature Humidity Logger For One Body Forming S...
HENGKO temperature and humidity probe consists of high precision RHTx series sensor module, one meter 4-pin cable, sintered metal filter cap, cable gland, et...
View Detail -
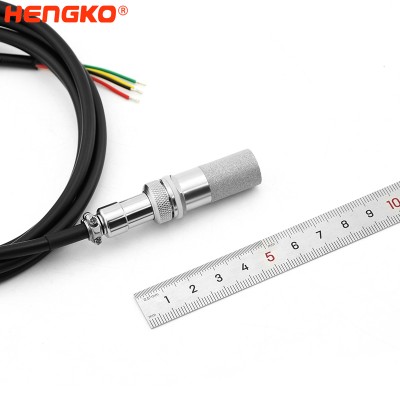

Temperature and Humidity Sensor Probe For Cold Chain Monitoring ± 0.1 ℃
±0.1℃ development of high precision, high stability temperature and humidity probe for cold chain monitoring. Foreign imports of moisture-sensitive temperatu...
View Detail -
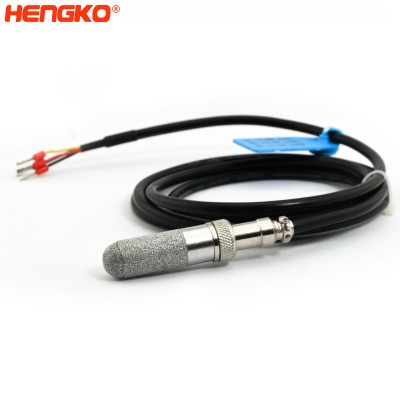

HT-P102 Temperature and Relative Humidity Probe
HENGKO temperature and relative humidity probe can be easily removed and replaced in the field without tools or adjust the transmitter,making it suitable fo...
View Detail -
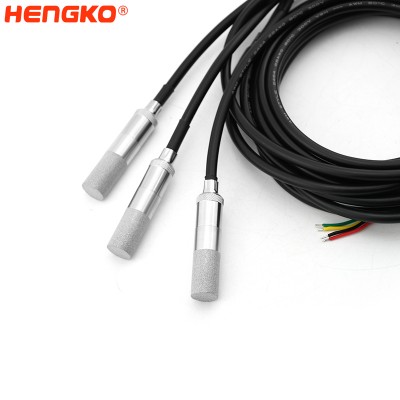

Economical Relative Humidity & Temperature Probes HT-P109 for industrial applications
An accurate, digitally-based relative humidity probe for use in higher performance applications. The temperature and humidity sensor senses, measures and rep...
View Detail -
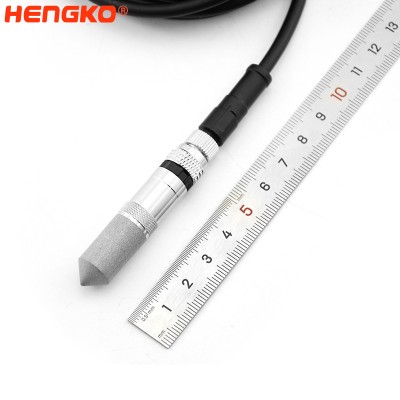

I2C Temperature and Humidity Probe with M8 Connector HT-P107
I2C M8 HT-P107: Precision temperature and humidity probe with M8 waterproof IP67 connector, dual dust filters, and I2C protocol. The I2C M8 HT-P107 is...
View Detail -
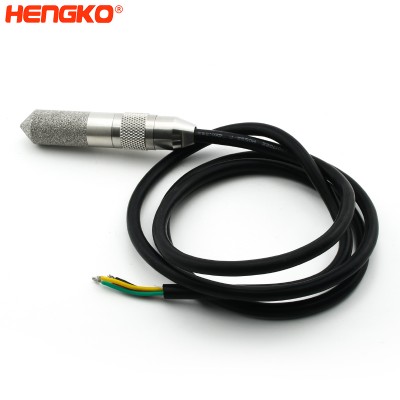

HT-P104 temperature and humidity sensor probe with knurled nut
An excellent ±2% relative humidity and ±0.5°C accuracy for most use. A cable type sensor in the digital temperature and humidity sensor series. Using the wor...
View Detail -
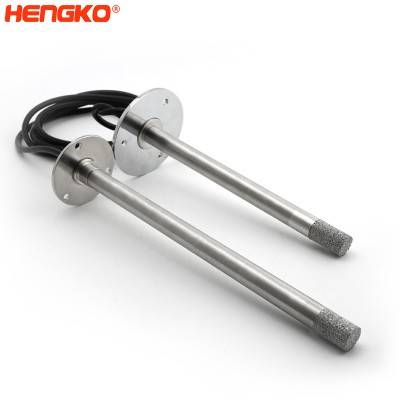

Flange Mounted irrigation temperature relative humidity sensor probe for in-line measur...
HENGKO flange mounted high temperature and relative humidity sensor probe is designed for in-line humidity measurement in industrial drying applications with...
View Detail -
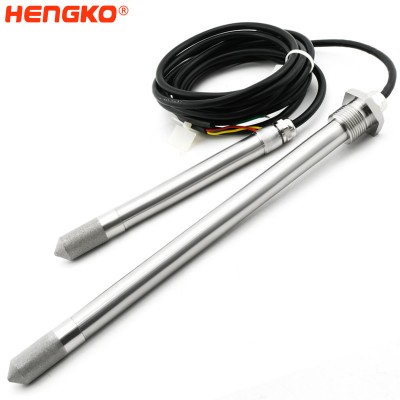

Relative RH Sensor Dew Point Probe For Baking Ovens Or High-temperature Dryers
HENGKO digital temperature and humidity module adopt high precision RHT series sensor equipped with a sintered metal filter shell for large air permeability,...
View Detail -
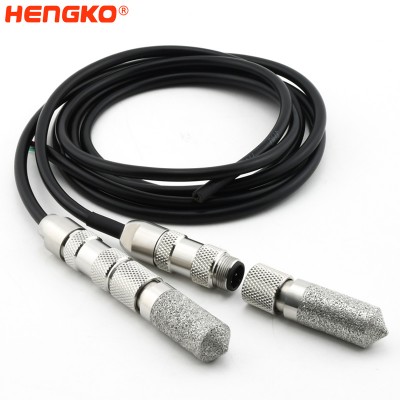

Waterproof IP66 RHT-H3X I2C exchengeable ±1.5%RH high accuracy temperature and humidity...
HENGKO relative humidity sensor probe is an anti-rust, robust, and precise RHT30 sensor, which can master enterprise-class and industrial-level applications....
View Detail -
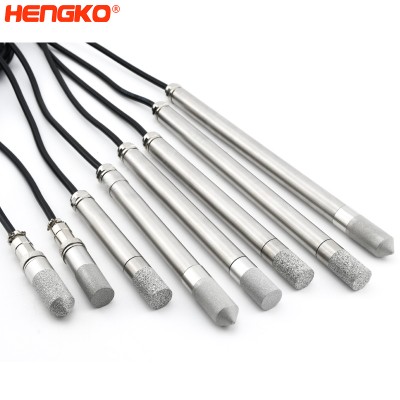

Durable weather-proof digital temperature and relative humidity sensor probe, SUS316 ho...
We offer high-accuracy RHT-H30 humidity sensor probes RHT-H31 humidity sensor probes and RHT-H35 humidity sensor probes. Our RH/T sensor probe can be used i...
View Detail -
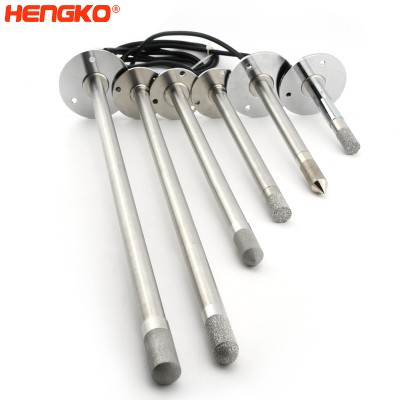

HENGKO sintered metal temperature and humidity sensor probe for grain blower
HENGKO temperature and humidity sensors can be applied in various fields: telepoint base stations, electronic control cabinets, production sites, storehouses...
View Detail -

Air temperature and relative humidity transmitter with porosity stainless steel probe p...
HT-802W/HT-802X temperature and humidity transmitter adopts wall-mounted waterproof housing. It is mostly used in the situation of bad outdoor and on-site en...
View Detail -
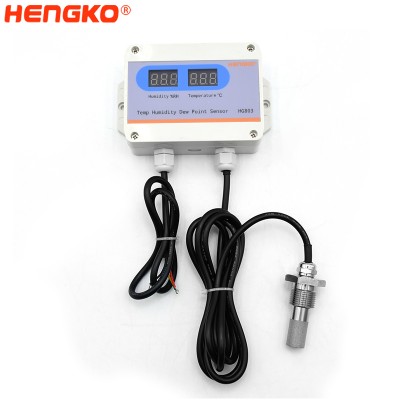

HG803 remote temperature and relative humidity transmitter with porous humidity probe p...
Product Describe HG803 Series Temperature and Humidity Monitor has been designed to measure, monitor and record temperature and humidity. It is a perfect sol...
View Detail -
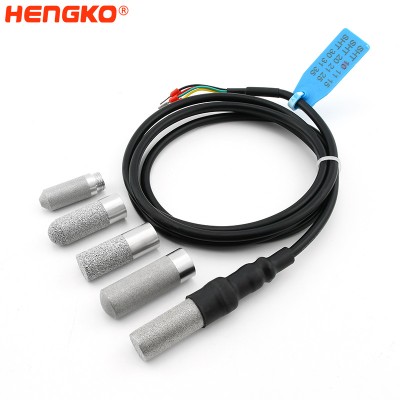

High Accuracy Low Consumption I2C Interface Temperature & Humidity relative Sensor...
HENGKO temperature and humidity sensor probe made with an IP66 protection grade high-tightness stainless steel sensor porous housing, it can be directly used...
View Detail -
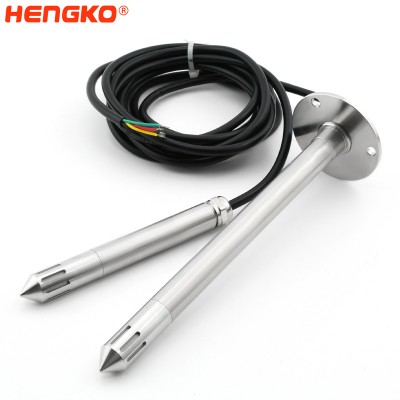

temperature and relative humidity sensor probe with stainless steel extension tube and ...
The HT-E067 relative humidity/ temperature transmitter provides a reliable and low-cost method for duct mount monitoring applications. Solid-state sensors pr...
View Detail -
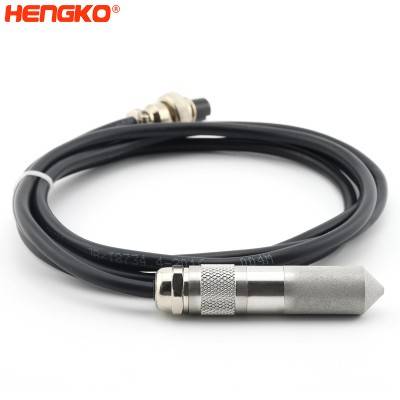

OEM I2C high precision air temperature and relative humidity sensor probe with stainles...
Temperature and relative humidity sensor probe HENGKO Humidity & Temperature Sensor is a fully-calibrated and temperature-compensated combined hum...
View Detail -
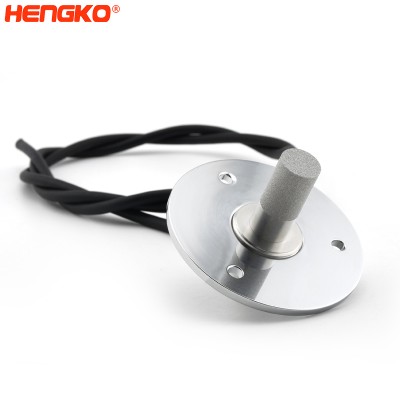

Flange Mounted digital waterproof high RHT-H serious I2C output temperature humidity se...
HENGKO IP67 Harsh Environment temperature and humidity probe is a fully-calibrated and temperature-compensated combined humidity and temperature sensor suppl...
View Detail
Types of Temperature Humidity Probe
There are four main types of temperature probes:
1. Thermocouples:
Thermocouples are the most common type of temperature probe. They are made of
two different metals that are joined together at one end. When the temperature changes, a voltage is produced
at the junction of the metals. This voltage is proportional to the temperature. Thermocouples are very versatile
and can be used to measure a wide range of temperatures, from -200°C to 2000°C.
2. Resistance temperature detectors (RTDs):
RTDs are made of a metal conductor, such as copper or nickel.
The resistance of the conductor changes
with temperature. This change in resistance can be measured and used to
calculate the temperature.
RTDs are more accurate than thermocouples, but they are also more expensive.
3. Thermistors:
Thermistors are semiconductors that exhibit a large change in resistance with temperature.
This makes them very sensitive to temperature changes. Thermistors are typically used to measure
temperatures over a narrow range, such as in medical devices or electronic circuits.
4. Semiconductor-based temperature sensors:
Semiconductor-based temperature sensors are the newest type of temperature probe. They are made of silicon or
other semiconductor materials and use a variety of physical effects to measure temperature. Semiconductor-based
temperature sensors are very accurate and can be used to measure a wide range of temperatures.
There are also two main types of humidity probes:
1. Capacitive humidity sensors:
Capacitive humidity sensors measure the change in capacitance of a capacitor as the humidity changes.
This change in capacitance is proportional to the humidity.
2. Resistive humidity sensors:
Resistive humidity sensors measure the change in resistance of a resistor as the humidity changes.
This change in resistance is proportional to the humidity.
Finally, The type of temperature or humidity probe that you choose will depend on your specific application.
Main Features
1. High Accuracy:
Sintered metal temperature probe are known for their high level of accuracy, which helps to ensure that the temperature measurements they provide are reliable and consistent.
2. Durability:
Because the probes are made from sintered metal, they can withstand high temperatures and harsh environments, making them suitable for various industrial and laboratory applications.
3. High Corrosion Resistance:
Sintered metal is highly resistant to corrosion, which makes these probes well-suited for use in environments where traditional thermocouples or RTDs may be prone to failure.
4. Faster Response Time:
Sintered metal temperature probes have a faster response time than many other temperature sensors, allowing for more accurate temperature measurements.
5. Wide Operating Temperature Range:
Wide range of temperatures, making them suitable for use in many different types of applications.
6. Customizable:
OEM factories like HENGKO can make custom solutions of the probe to customers' specifications; it can be adjusted to fit their specific requirements and applications.

6 Steps to Custom / OEM Sintered Temperature Probe
1. Define the Application:
The first step in creating a custom sintered metal temperature probe is clearly defining the application for which it will use. It includes understanding the environment in which the probe will be used, the temperature range it will need to measure, and any other requirements that need to be met.
2. Select a Material:
The next step is to select a material for the probe. Sintered metal temperature probes are typically made from various materials, including steel, stainless steel, and nickel. Each material has unique properties, so choosing one well-suited for the specific application is important.
3. Design the Probe:
Once the material has been selected, the next step is to design the probe. It includes determining the size and shape of the probe, as well as the location of the temperature-sensing element.
4. Test the Probe:
Before mass production, you'd better test it to ensure it meets all of the required specifications. It includes performing various tests to ensure that the probe is accurate, reliable, and able to withstand the harsh environments in which it will use it.
5. Mass Production:
Once the probe has been designed and tested, it's ready to be mass-produced. It typically involves using specialized equipment to create large quantities of the probe so it can be readily available for purchase.
6. Package and Delivery:
The final step is shipping the probes to the customer. Usually includes careful packaging to ensure that it will not damage the probes during transport and logistics to deliver the probes to the customer.

Main Application
1. Industrial Process Control:
Sintered metal temperature probes are commonly used in industrial process control. They measure the temperature of gases and liquids to optimize process conditions and ensure quality control.
2. Power generation:
In power generation, metal temperature probes are used to measure the temperature of steam, combustion gases, and other fluids used in power plants.
3. Oil and gas exploration:
Sintered metal temperature probes are used to measure the temperature of drilling fluids, wellbores, and other fluids in the oil and gas exploration industry.
4. Metallurgy and metalworking:
The probes are used to measure the temperature of molten metals, furnace linings, and other materials in the metallurgy and metalworking industries.
5. Aerospace and aviation:
Sintered metal temperature probes are used to measure the temperature of jet engine components, avionics, and other equipment in the aerospace and aviation industries.
6. Automotive and transportation:
The probes are used to measure the temperature of engines, transmissions, and other vehicle components in the automotive and transportation industries.
7. Medical:
For medical equipment such as MRI machines, CT scanners, and other imaging equipment to measure the temperature of the patient, temperature probe can also used in various devices.
8. Research and Development:
Sintered metal temperature probes are also used in research and development laboratories, where they are used to measure the temperature of various materials and conduct experiments in a wide range of fields, including chemistry, physics, and biology.
FAQ for Temperature Probe
1. What is a temperature probe?
A temperature probe is a device used to measure temperature. Many different temperature probes exist, including thermocouples, RTDs, and sintered metal temperature probes.
2. How does a sintered metal temperature probe work?
A sintered metal temperature probe works by using the principle of thermal expansion. The sensing element in the probe is made from a sintered metal, which expands and contracts as the temperature changes. This movement is then converted into an electrical signal, which can be read and interpreted by a temperature measurement instrument.
3. What are the advantages of using a sintered metal temperature probe?
Sintered metal temperature probes offer several advantages over traditional temperature probes, such as those made from glass or ceramics. These advantages include:
1. Durability:
Sintered metal probes are extremely durable and can withstand harsh environments, including high temperatures, corrosive chemicals, and physical shock. This makes them ideal for use in industrial applications where reliability and robustness are essential.
2. High Strength:
Sintered metal probes are incredibly strong and can withstand high pressures without breaking or deforming. This makes them suitable for applications where the probe may be subjected to mechanical stress or impact.
3. Thermal Conductivity:
Sintered metal probes have excellent thermal conductivity, allowing them to quickly and accurately measure temperature changes. This is crucial for applications where precise temperature monitoring is critical.
4. Chemical Resistance:
Sintered metal probes are resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making them suitable for use in harsh environments where chemical exposure is a concern.
5. Electrical Conductivity:
Sintered metal probes can be electrically conductive, allowing them to be used for applications where electrical signals are required.
6. Formability:
Sintered metal probes can be formed into various shapes and sizes to meet specific application requirements.
7. Scalability:
Sintered metal probes can be mass-produced in a cost-effective manner, making them suitable for high-volume applications.
8. Biocompatibility:
Sintered metal probes can be made from biocompatible materials, making them suitable for use in medical applications.
Overall, sintered metal temperature probes offer a combination of durability, high strength, thermal conductivity, chemical resistance, electrical conductivity, formability, scalability, and biocompatibility, making them a versatile and advantageous choice for a wide range of applications.
4. What are the typical applications of sintered metal temperature probes?
Sintered metal temperature probes are commonly used in industrial process control, power generation, oil and gas exploration, metallurgy and metalworking, aerospace and aviation, automotive and transportation, medical equipment, and research and development.
5. What are the disadvantages of using a sintered metal temperature probe?
Sintered metal temperature probes are more expensive than other temperature sensors and may not be suitable for all applications. They also tend to be less stable and inaccurate over a long period.
6. How do I choose the right sintered metal temperature probe for my application?
When choosing a sintered metal temperature probe, it's important to consider the application's specific requirements. It includes the temperature range that the probe will need to measure, the environment in which the probe will be used, and any other requirements that need to be met.
7. Can sintered metal temperature probes be used in high-temperature applications?
Yes, sintered metal temperature probes can operate at high temperatures, making them well-suited for use in a wide range of applications.
8. Can sintered metal temperature probes be used in corrosive environments?
Yes, sintered metal temperature probes can be used in corrosive environments. This is because sintered metals are typically made from materials that are resistant to corrosion, such as stainless steel, Hastelloy, and Inconel. These materials can withstand exposure to a wide range of corrosive chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and solvents.
In addition to being resistant to corrosion, sintered metal temperature probes are also very durable and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. This makes them ideal for use in harsh industrial environments where corrosion is a concern.
Here are some specific examples of how sintered metal temperature probes are used in corrosive environments:
1. Chemical processing:
Sintered metal temperature probes are used to monitor the temperature of chemical reactions in a variety of industrial processes.
2. Metal refining:
Sintered metal temperature probes are used to monitor the temperature of molten metals during the refining process.
3. Power generation:
Sintered metal temperature probes are used to monitor the temperature of steam and flue gases in power plants.
4. Oil and gas production:
Sintered metal temperature probes are used to monitor the temperature of oil and gas wells.
5. Semiconductor manufacturing:
Sintered metal temperature probes are used to monitor the temperature of furnaces and other equipment during semiconductor manufacturing.
If you are considering using sintered metal temperature probes in a corrosive environment, it is important to choose a probe that is made from a material that is compatible with the chemicals that will be present. You should also consult with a supplier of sintered metal temperature probes to get more information about the specific properties of the probes that they offer.
9. Are sintered metal temperature probes more accurate than other types of temperature sensors?
Sintered metal temperature probes are known for their high level of accuracy, which helps to ensure that the temperature measurements they provide are reliable and consistent.
10. How long do sintered metal temperature probes last?
The lifespan of a sintered metal temperature probe will depend on the application and environment in which it is used. The life of the sintered metal temperature probe can be from several months to a few years.
11. How should I maintain my sintered metal temperature probe?
To ensure the longevity and accuracy of your sintered metal temperature probe, it is important to perform regular maintenance and calibration. It is also important to properly store and handle the probes and protect them from damage or contamination.
12. Can I customize a sintered metal temperature probe according to my specific requirements?
Many manufacturers offer customers custom solutions according to their specific requirements and applications. You can consult with the manufacturer and discuss your requirement to make the probe that best suits your needs.
Don't hesitate to reach out to us! If you have any questions about our sintered
metal temperature probes, or if you're interested in learning more about how
we can help you, please contact us via email at ka@hengko.com