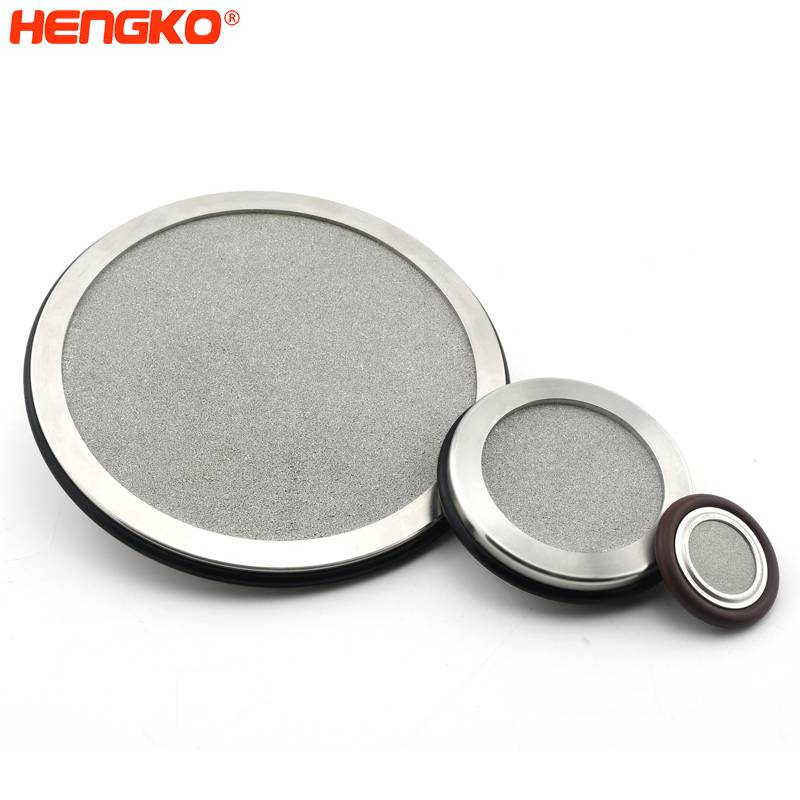
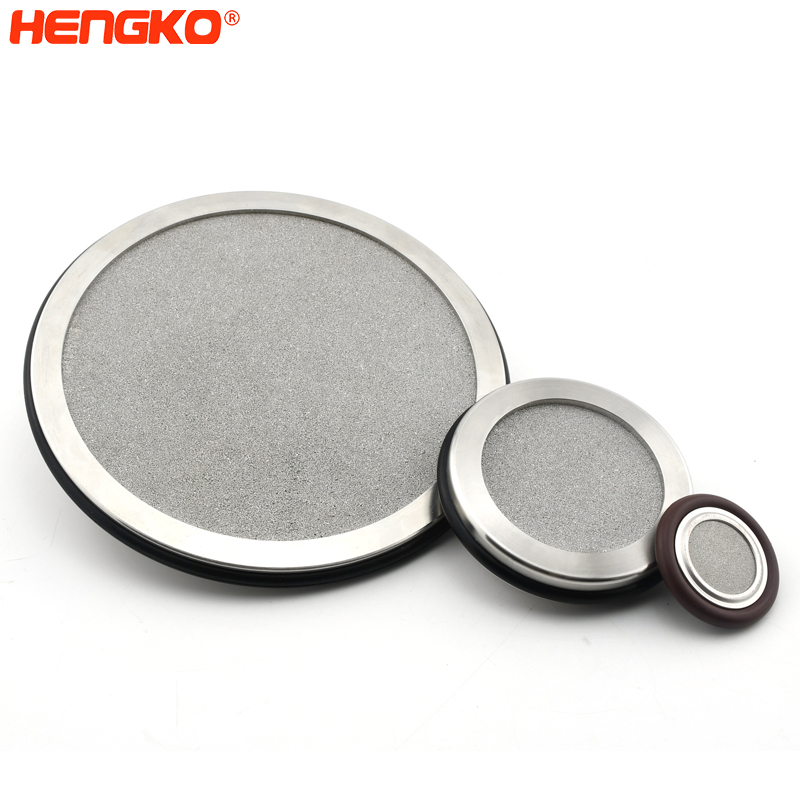
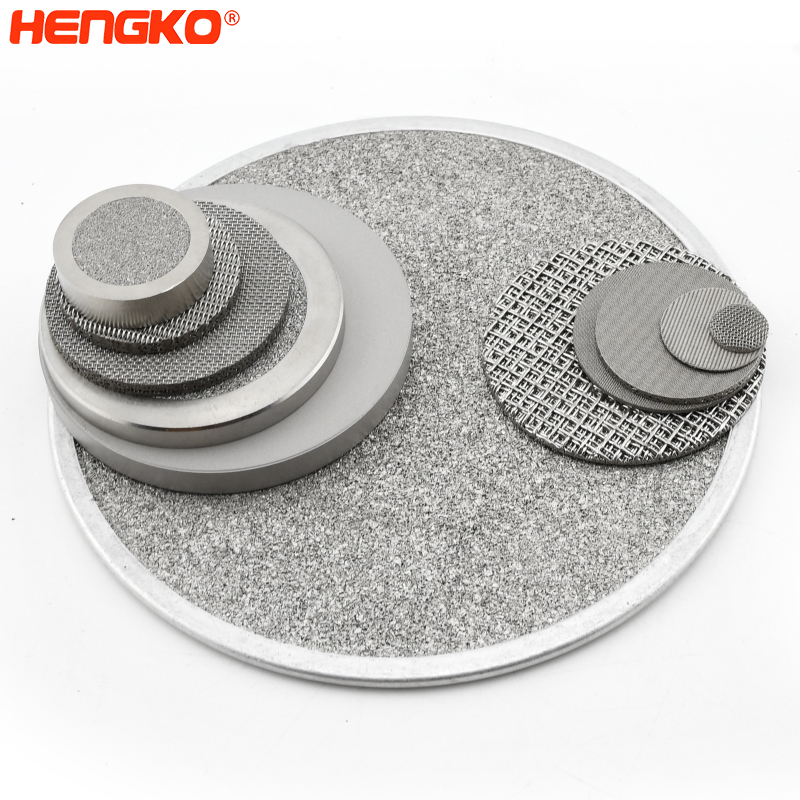
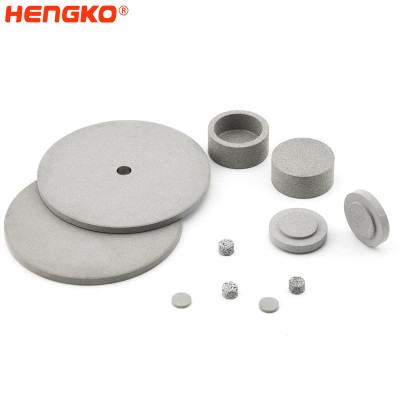
Porous sintered metal filter of ozone and air in water
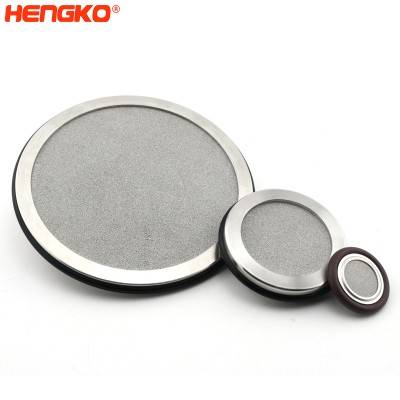
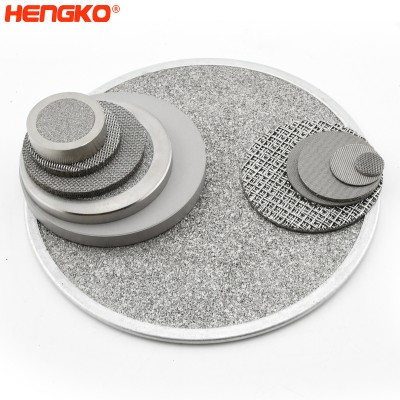
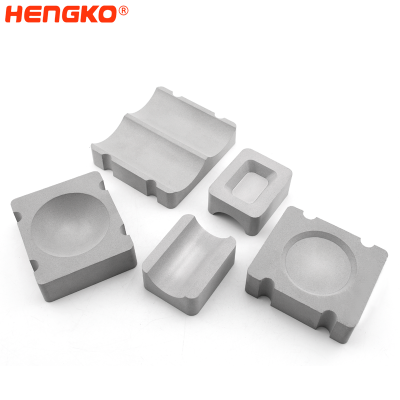
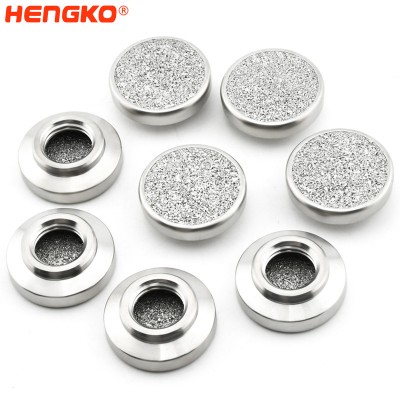
 The manufacturing process of large diameter (80-300 mm) discs of sintered stainless and corrosion-resistant steels is described. The characteristics of the initial powder and the sintered disc are described, and the dimensions of the formed bubbles are examined according to the parameters of the pore structure. Its porous disc is made of stainless steel porous powder, while its housing and components are corrosion-resistant steel. In drinking water treatment systems, the use of sintered dispersers makes it possible to reduce the amount of ozone and gas that must be injected during the treatment process while maintaining the same level of purification.
The manufacturing process of large diameter (80-300 mm) discs of sintered stainless and corrosion-resistant steels is described. The characteristics of the initial powder and the sintered disc are described, and the dimensions of the formed bubbles are examined according to the parameters of the pore structure. Its porous disc is made of stainless steel porous powder, while its housing and components are corrosion-resistant steel. In drinking water treatment systems, the use of sintered dispersers makes it possible to reduce the amount of ozone and gas that must be injected during the treatment process while maintaining the same level of purification.
The method of ozonation has been widely used in technologies designed to treat drinking water, break down toxic industrial wastes, and bleach cellulose and natural fibres. The method is based on the saturation of water with ozone.
Decomposing into atomic oxygen, the ozone oxidizes all organic and metallic contaminants and kills microorganisms and viruses. During flotation and the biochemical purification of effluents, air bubbles move solid particles to the surface of the water and stimulate the decomposition of organic compounds by activated sludge. Water is saturated with ozone or air by using tubular and flat porous dispersers made of different materials, which combine a high degree of saturation efficiency with low energy use.
The dissolution process of oxygen in water is governed by the degree of dispersion of the gas phase, i.e., by the size and number of bubbles. A decrease in bubble size is accompanied by an increase in the size of the phase boundary, a reduction in the rate at which the bubbles rise to the surface and, thus, an increase in the length of time the gas is in contact with the water.
Porous sintered metal filter of ozone and air in water

Can't find a product that meets your needs? Contact our sales staff for OEM/ODM customization services!