-
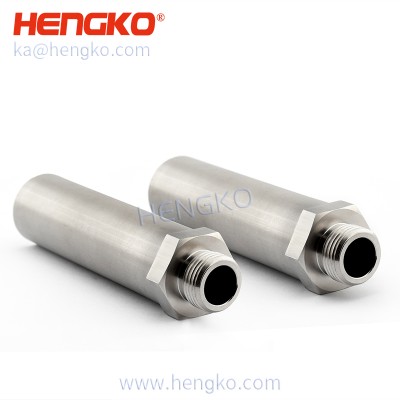

25 Micron Stainless Steel 316L Porous Metal Sintered Filter Cartridge for Gas Liquid So...
Product Describe HENGKO stainless steel filter tubes are made by sintering 316L powder material or multilayer stainless steel wire mesh in high temperatures....
View Detail -
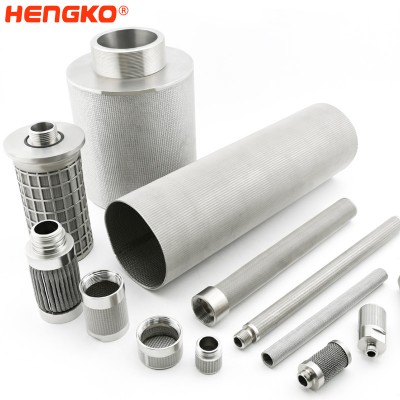

Customized medical 304 316 316L stainless steel filter mesh cartridges from HENGKO
Made of a multi-layer sintered 316 or 304 stainless steel strainer, it has the properties of heat resistance, pressure resistance, and corrosion resistance.T...
View Detail -
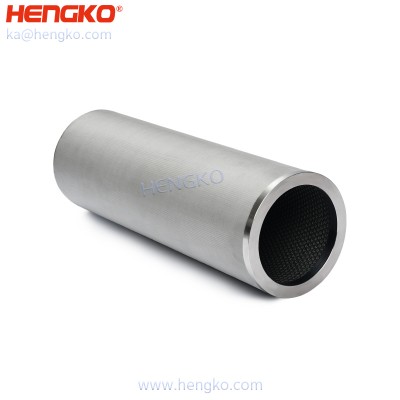

High pressure resistant 316l sintered stainless steel wire mesh filter cartridge
Sinter wire mesh filters are usually used for purification and filtration of liquid and gas, separation and recovery of solid particle, transpiration cooling...
View Detail -
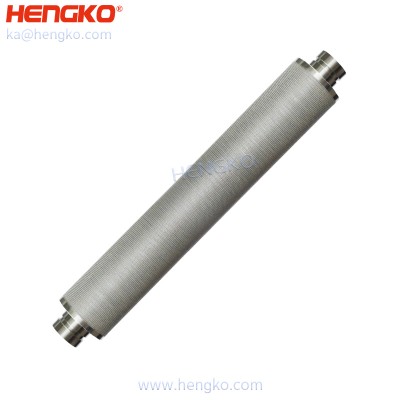

Micro powder sintered 304 316L stainless steel industrial dust collector oil filter car...
Candle filters and porous tubes are long, cylindrical filters with thin walls, i.e. they have a high length-to-diameter ratio. The cylinders can be hollow or...
View Detail -
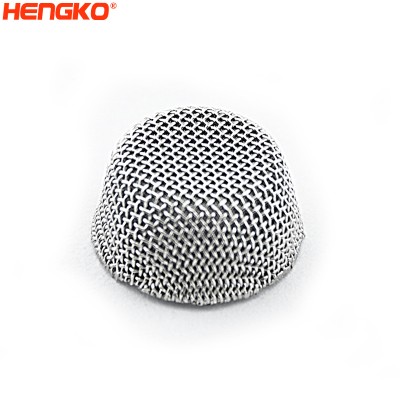

sintered stainless steel wire mesh air filter cartridge for dust removal or pure water
Sinter wire mesh filters are usually used for purification and filtration of liquid and gas, separation and recovery of solid particles, transpiration coolin...
View Detail -
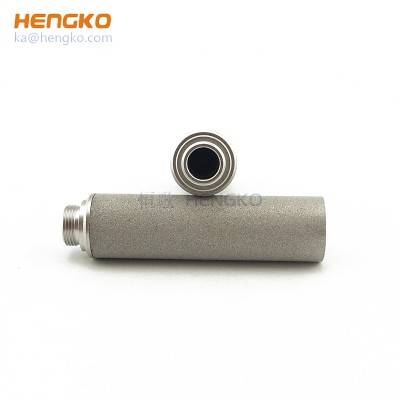

precision sintered micron porous metal bronze SS 316 stainless steel filter candle powd...
Product Describe HENGKO stainless steel filter elements are made by sintering 316L powder material or multilayer stainless steel wire mesh at high temperatur...
View Detail -
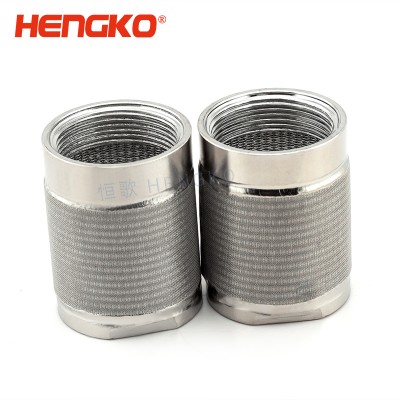

micron sintered 316L stainless steel single cartridge filter for oil water treatment
Sintered wire mesh filters are usually used for purification and filtration of liquid and gas, separation and recovery of solid particles, transpiration cool...
View Detail -
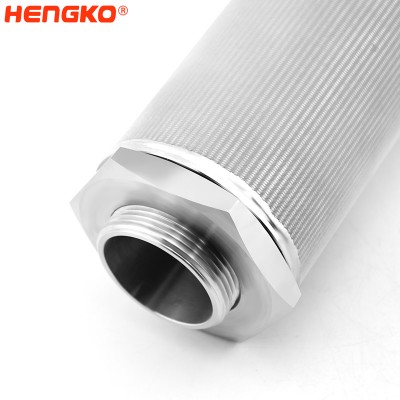

Reusable Resists High Temperature Microns Mesh Sintering Metal Filter Cartridge
Sinter wire mesh filters are usually used for purification and filtration of liquid and gas, separation and recovery of solid particles, transpiration coolin...
View Detail -
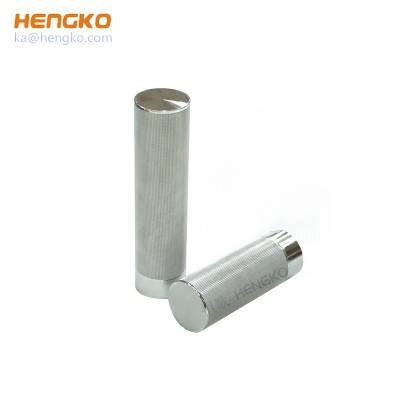

Candle type Sintered 316L stainless steel mesh filter reusable cartridge
HENGKO offers an extensive collection of stainless steel filter cartridges that are tailored for use in a broad range of industries, including petrochemicals...
View Detail -
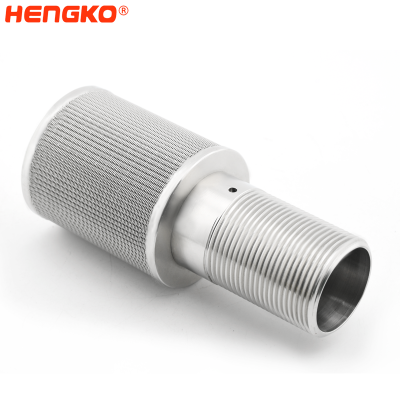

5 40 micron sintered stainless steel porous metal fuel oil/air/dust filter wire mesh ca...
Sinter wire mesh filters are usually used for purification and filtration of liquid and gas, separation and recovery of solid particles, transpiration coolin...
View Detail -
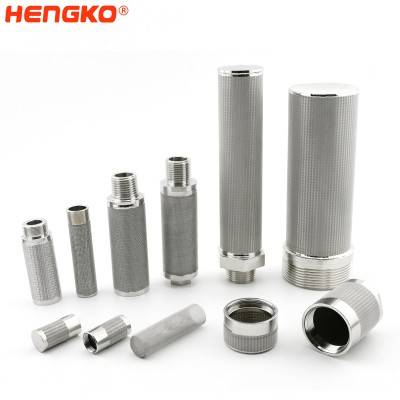

Compressed air stainless steel wire mesh filter cartridge for sterile process air and g...
Sintering is a process that entails the application of heat and pressure to bond the contact points of all wires together to form a securely fused wire mesh ...
View Detail -
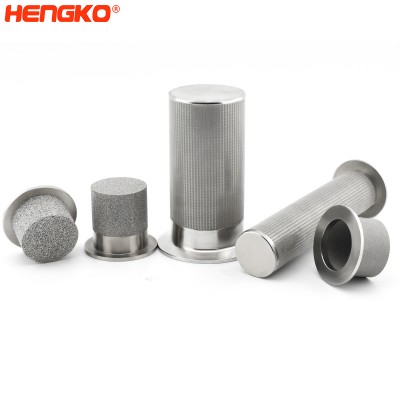

1.0-100um sintered porous metal stainless steel cartridge filter mesh perform in liquid...
Sinter wire mesh filters are usually used for purification and filtration of liquid and gas, separation and recovery of solid particles, transpiration coolin...
View Detail -
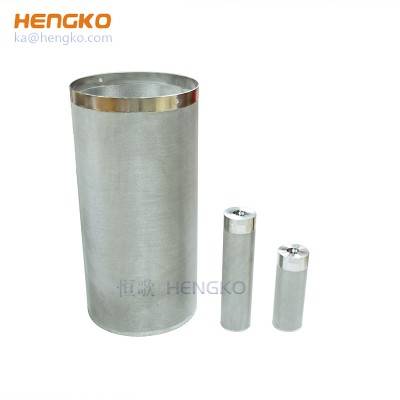

Anti-corrosion Microns Powder Porous Sintered Metal Filter Cartridge For Filtration System
HENGKO creates porous filter tubes that offer versatility in design as they can be hollow or blind with a minimum wall thickness of 1mm. These products are c...
View Detail -
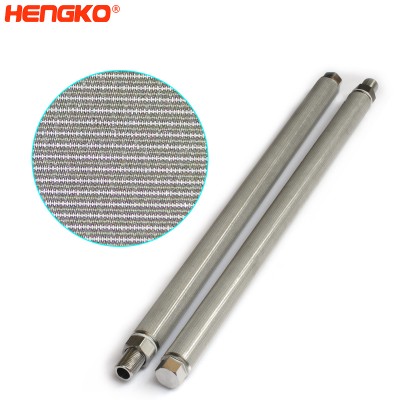

porous metal stainless steel cartridge filter for high pressure air purification solid ...
HENGKO manufactures its porous metal materials by heat treating 316L powder material or multilayer stainless steel wire mesh at elevated temperatures. Their ...
View Detail -
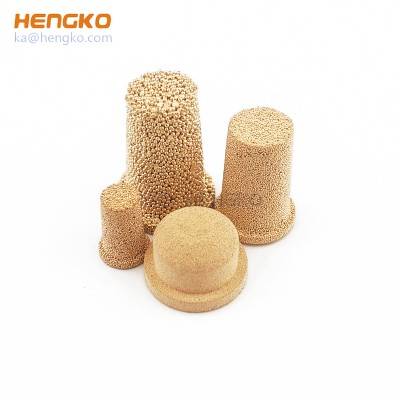

High temperature resistance pressure reusable microns porous metal bronze brass filter ...
HENGKO porous filter tubes can be hollow or blind and have a minimum wall thickness of 1 mm. They are made by isostatic compaction of powder in a flexible mo...
View Detail -
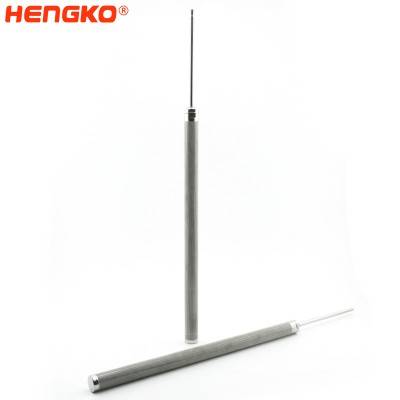

Sintered Filter Cartridges for Medical Filtration Applications -HENGKO
HENGKO has developed an all-metal sterilizing grade membrane for medical filtration applications. This material is ideally suited for applications in medical...
View Detail
What are Porous Sintered Metal Filters used for ?
Porous sintered metal filters are highly versatile and find applications across a range of industries
due to their durability, resistance to high temperatures and pressures, and the ability to withstand
corrosive environments. Here are some common uses for these filters:
1. Filtration Applications:
* Gas Filtration:
2. Catalyst Recovery:
In chemical reactors, sintered metal filters are used to recover expensive catalysts used in the reaction process
3. Sparging and Gas Diffusion:
These filters are used in bioreactors and fermentation processes to introduce gases into liquids in a controlled,
4. Venting Applications:
In automotive and aerospace industries, sintered metal vents protect sensitive equipment by equalizing pressures
5. Fluidization:
Used in powder handling industries to fluidize bulk powders, ensuring smooth flow and preventing clogging
6. Aerosol Sampling:
Sintered metal filters are used in environmental monitoring equipment to collect aerosol samples for analysis,
7. Heat Exchange:
Due to their high thermal conductivity and resistance to temperature swings, these filters are also used in
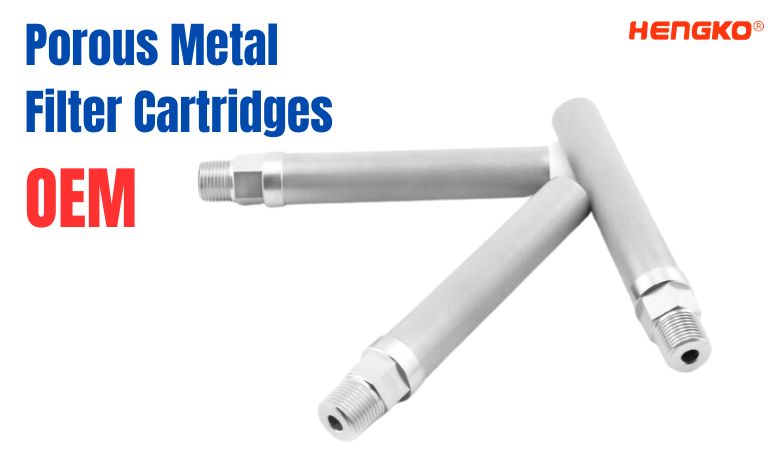

Main Features of Porous Metal Filter Cartridges :
1. Material Composition
Porous metal filters are typically made from sintered metals such as stainless steel (304, 316L),
titanium, and other alloys like Hastelloy and Inconel. This composition provides excellent
mechanical strength and resistance to corrosion and thermal shock.
2. Controlled Porosity
The manufacturing process allows for precise control over pore size, ranging from 0.5 to 200 microns.
This control facilitates the filtration of particles at various levels, making them suitable for microfiltration
of gases and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
3. High Strength and Durability
These filters can withstand high differential pressures (up to 3000 psi) and harsh operating conditions,
ensuring long service life and reliability in demanding applications.
4. Cleanability and Reusability
Porous metal filter cartridges are designed to be cleaned and reused, often through methods like
backflushing or ultrasonic cleaning. This feature not only reduces operational costs but also
enhances their longevity.
5. Thermal and Chemical Resistance
These filters maintain performance in extreme temperatures (up to 930°C) and are resistant to a wide range
of chemicals, making them ideal for applications in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food and
beverage industries.
6. Customization Options
Manufacturers offer customization in terms of material, pore size, and dimensions to meet specific
application requirements.
This flexibility allows for optimal performance tailored to the needs of different industries.
7. Low Pressure Drop
The design of porous metal filters ensures a low pressure drop across the filter medium, which enhances
flow rates and overall system efficiency while minimizing energy consumption.
8. Versatile Applications
These filters are utilized in various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, and power
generation, for applications such as filtration, flow control, and noise reduction.
In summary, porous metal filter cartridges are engineered for high performance and versatility, making
them essential components in many industrial filtration systems.
Their robust construction and ability to be customized for specific applications ensure they meet the
rigorous demands of modern manufacturing processes.
Types of Porous Metal Filter Cartridges
Porous metal filter cartridges are widely used in various industries due to their excellent filtration properties,
durability, and chemical resistance. They are typically constructed from sintered metal powders, such as
stainless steel, bronze, or nickel.
Here are some common types of porous metal filter cartridges:
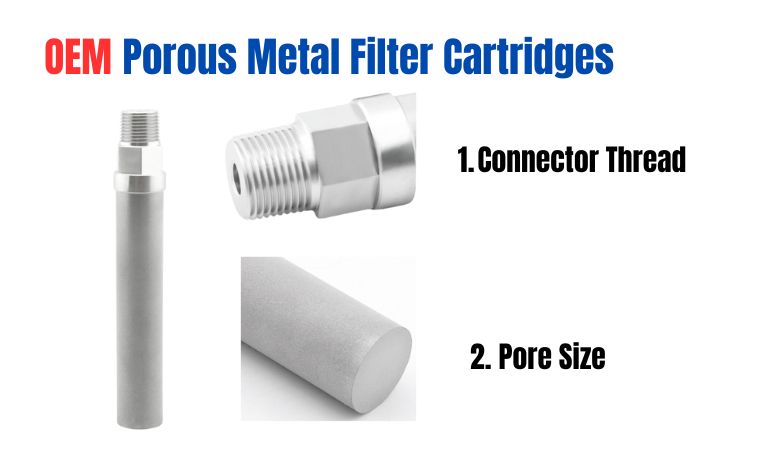
1. Based on Pore Size:
*Coarse: Larger pore sizes, suitable for removing larger particles like dirt, sand, and debris.
*Fine: Smaller pore sizes, ideal for removing finer particles like bacteria, viruses, and colloids.
*Ultrafine: Extremely small pore sizes, used for ultra-filtration applications, such as removing dissolved solids and impurities.
2. Based on Shape:
*Cylindrical: The most common shape, offering a large surface area for filtration.
*Pleated: Folded or pleated design, increasing the filtration area and improving efficiency.
*Disc: Flat, disc-shaped cartridges, suitable for specific applications or equipment.
3. Based on Material:
*Stainless Steel: The most common material due to its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and high-temperature tolerance.
*Bronze: Offers good corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, often used in heat exchange applications.
*Nickel: Provides excellent chemical resistance and high-temperature performance, suitable for harsh environments.
*Other Metals: Depending on specific requirements, other metals like titanium, aluminum, or tungsten can be used.
4. Based on Filtration Mechanism:
*Depth Filtration: Particles are trapped within the porous structure of the filter.
*Surface Filtration: Particles are captured on the surface of the filter.
*Sieve Filtration: Particles are physically blocked by the pore size.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Porous Metal Filter Cartridge:
*Particle Size: The size of the particles to be removed.
*Flow Rate: The required flow rate through the filter.
*Pressure Drop: The allowable pressure drop across the filter.
*Chemical Compatibility: The compatibility of the filter material with the fluid being filtered.
*Temperature: The operating temperature of the filter.
*Cleaning and Regeneration: The method and frequency of cleaning or regenerating the filter.
By understanding these different types and factors, you can select the most appropriate porous metal filter cartridge for your specific filtration needs.
How to Choose Right Porous Metal Filter Cartridges ?
There are many factors you should consider when choose right porous metal filter cartridges
for your filter equipment or project. Here we list 8 main key points you should check.
1. Particle Size:
*Determine the size of the particles you need to remove.
*Select a cartridge with a pore size that is smaller than the particles to be filtered.
2. Flow Rate:
*Consider the required flow rate through the filter.
*Choose a cartridge with a surface area and pore size that can handle the desired flow rate
without excessive pressure drop.
3. Pressure Drop:
*Evaluate the allowable pressure drop across the filter.
*Select a cartridge with a low pressure drop to minimize energy consumption and ensure efficient operation.
4. Chemical Compatibility:
*Assess the chemical compatibility of the filter material with the fluid being filtered.
*Choose a cartridge made from a material that is resistant to corrosion and chemical attack by the fluid.
5. Temperature:
*Determine the operating temperature of the filter.
*Select a cartridge that can withstand the expected temperature range without compromising its performance or integrity.
6. Cleaning and Regeneration:
*Consider the method and frequency of cleaning or regenerating the filter.
*Choose a cartridge that is easy to clean or regenerate, depending on the specific application and cleaning requirements.
7. Filter Media:
*Evaluate the type of filter media used in the cartridge.
*Consider options like sintered metal powders, woven wire mesh, or other porous materials, based on your specific needs.
8. Cartridge Design:
*Assess the cartridge design, such as cylindrical, pleated, or disc-shaped.
*Select a design that is compatible with your equipment and offers the desired filtration performance.
9. Manufacturer and Quality:
*Research reputable manufacturers of porous metal filter cartridges.
*Choose a cartridge from a manufacturer with a proven track record of quality and reliability.
FAQ
1. What are porous metal filter cartridges and how do they work?
Porous metal filter cartridges are filtration devices made from sintered metals that possess a rigid, porous structure.
These cartridges are typically constructed by compacting metal powders under high temperatures and pressures to form a solid,
yet porous, material. The porosity can be precisely controlled to target specific particle sizes.
As fluids or gases pass through the filter, particles larger than the pore size are trapped, effectively removing them from the stream.
This mechanism is crucial for applications requiring high purity and efficiency, such as in pharmaceutical manufacturing,
chemical processing, and critical fluid management systems.
2. What materials are commonly used in the manufacturing of porous metal filter cartridges?
The most commonly used materials for making porous metal filter cartridges include stainless steel, titanium, and nickel alloys.
These materials are chosen for their robust mechanical properties, excellent corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme
temperatures and pressures. Stainless steel is widely favored for general applications due to its durability and cost-effectiveness,
while titanium and nickel alloys are preferred in environments that are highly corrosive or require greater strength-to-weight ratios.
3. What are the main advantages of using porous metal filter cartridges over other types of filters?
Porous metal filter cartridges offer several distinct advantages:
*High Temperature Resistance: They can operate effectively under high-temperature conditions, which is essential for processes like hot gas filtration and catalysis.
*Chemical Resistance: Metal filters are inert to most chemicals, making them suitable for harsh chemical environments where polymer filters would degrade.
*Strength and Durability: Metal filters can withstand high pressures and severe mechanical stresses without deforming or breaking.
*Regenerable and Reusable: They can be cleaned and reused multiple times, offering a long service life and reducing replacement costs and waste.
*Customizable: The porosity and geometric design can be customized to meet specific filtration needs, providing flexibility across various applications.
4. In what applications are porous metal filter cartridges most commonly used?
Porous metal filter cartridges are extensively used in several critical applications, including:
*Chemical Industry: For the filtration of high-purity chemicals and protection of catalyst beds from particulate contamination.
*Pharmaceuticals: In the production of APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) where contamination control is crucial.
*Food and Beverage: For sterile filtration processes to ensure product safety and quality.
*Oil and Gas: In upstream and downstream processing to remove particulates from fuels and protect sensitive equipment.
*Aerospace and Automotive: For filtration of hydraulic fluids and fuels under extreme operating conditions.
5. How are porous metal filter cartridges maintained and cleaned?
The maintenance and cleaning of porous metal filter cartridges depend largely on the type of contamination and the physical
properties of the filter material. Common cleaning methods include:
*Backflushing: Reversing the flow direction to dislodge particles.
*Ultrasonic Cleaning: Using high-frequency sound waves to remove fine particulates.
*Chemical Cleaning: Employing solvents or acids to dissolve contaminants.
*High-Temperature Burnout: Using heat to oxidize organic materials.
Regular maintenance and proper cleaning can significantly extend the life of the filter cartridges, making them a cost-effective solution in many industrial applications.





















