1. Why Use Gas Flow Restrictor ?
Gas flow restrictors are used for several important reasons in various applications involving gases. Here are some key reasons why gas flow restrictors are utilized:
1. Safety: Gas flow restrictors play a crucial role in ensuring safety by limiting the flow rate of gases in systems. By controlling the flow, they prevent excessive gas release, which could lead to hazardous conditions, explosions, or equipment damage.
2. Regulation: Flow restrictors help regulate gas flow rates, ensuring that the system operates within the desired parameters. This is essential for maintaining process stability and efficiency.
3. Pressure Control: Gas flow restrictors can be used to manage gas pressure in the system. By creating a pressure drop, they help maintain safe operating conditions and prevent over-pressurization.
4. Precision and Accuracy: In applications that require precise gas dosing or metering, flow restrictors offer a controlled and accurate flow, ensuring consistent results.
5. Conservation of Gas: In processes where gas conservation is essential, flow restrictors are employed to limit gas consumption and reduce waste.
6. Calibration and Testing: Gas flow restrictors are utilized as part of calibration and testing procedures to validate the accuracy of gas flow measurement devices.
7. Gas Mixing: Flow restrictors can be used in gas mixing applications, ensuring the correct proportions of different gases are combined for specific processes.
8. Prevent Gas Saturation: In certain applications, excessive gas flow can lead to gas saturation, reducing the effectiveness of the process. Flow restrictors prevent such saturation and maintain optimal conditions.
9. Equipment Protection: Restricting gas flow can help protect downstream equipment from damage or performance issues caused by high flow velocities.
10. Flow Conditioning: In some cases, gas flow restrictors are employed to condition the gas flow, ensuring it is uniform and stable before entering critical components or processes.
Gas flow restrictors come in various forms, including orifice plates, needle valves, flow control valves, and capillary tubes, among others. The specific type of flow restrictor used depends on the application's requirements, gas properties, flow rates, and pressure conditions.
Whether it's in industrial processes, gas handling systems, research laboratories, or other applications, gas flow restrictors are essential tools for ensuring safe, controlled, and efficient gas flow management.
2. Types of Gas Flow Restrictor
There are various types of gas flow restrictors, each designed to suit different applications and gas flow control requirements. Here are some common types of gas flow restrictors:
1. Orifice Plate:
An orifice plate is a simple, cost-effective device with a precisely sized hole that creates a pressure drop, restricting gas flow. It is widely used for gas flow control in industrial applications.
2. Needle Valve:
Needle valves have a tapered needle-like stem that can be adjusted to control the gas flow rate with high precision. They are commonly used when fine control over the gas flow is necessary.
3. Flow Control Valve:
Flow control valves are designed to regulate gas flow by adjusting the valve opening. They can be manual, automatic, or electronically controlled, offering versatility in flow control applications.
4. Capillary Tube:
Capillary tubes are small-diameter tubes used to restrict gas flow in a controlled manner. They are often used for precise gas dosing or in small-scale applications.
5. Flow Restrictor Nozzle:
Flow restrictor nozzles use a narrow opening or nozzle to limit the gas flow rate. They find applications in gas-saving devices and specialized gas flow control systems.
6. Adjustable Restrictors:
These restrictors allow for manual adjustment of the flow rate by changing the orifice size or other variables, providing flexibility in gas flow control.
7. Fixed Restrictors:
Fixed restrictors have a predetermined fixed size of the flow passage, making them suitable for applications requiring a constant gas flow rate.
8. Sintered Metal Filters:
Sintered metal filters serve as gas flow restrictors by virtue of their porous structure. They offer controlled flow rates and filtration capabilities simultaneously.
9.. Flow Control Orifices:
These flow restrictors have a specially designed shape to achieve specific gas flow characteristics, such as laminar flow or pressure drop control.
10. Laminar Flow Elements:
Laminar flow elements utilize laminar flow principles to control gas flow rates accurately and linearly.
11. Gas Mass Flow Controllers:
Mass flow controllers are sophisticated devices that measure and control gas flow rates precisely, offering accuracy and repeatability in various gas flow applications.
The choice of gas flow restrictor depends on factors such as the type of gas being used, the required flow rate, pressure conditions, and the level of control needed for the specific application. Proper selection and installation of the appropriate gas flow restrictor are crucial to achieving optimal performance and safety in gas flow processes.
3. Main Features of Gas Flow Restrictor
Gas flow restrictors come with several features that make them valuable tools in controlling gas flow in various applications. Here are the main features of gas flow restrictors:
1. Flow Control:
Gas flow restrictors enable precise control over the rate of gas flow, allowing for accurate adjustment and regulation according to specific requirements.
2. Pressure Drop:
They create a pressure drop in the gas flow, which is essential for maintaining safe and controlled operating conditions in the system.
3. Gas Conservation:
Gas flow restrictors help conserve gas by limiting excessive flow rates, reducing waste, and optimizing gas consumption.
4. Flow Stability:
Gas flow restrictors ensure flow stability, preventing fluctuations or surges in the gas flow that may adversely affect downstream processes or equipment.
5. Safety:
By controlling gas flow rates, they contribute to enhanced safety, preventing over-pressurization or gas-related hazards in the system.
6. Accuracy:
Gas flow restrictors provide accurate flow rate control, making them suitable for applications that demand precision and consistency.
7. Versatility:
They can be used with various gases, accommodating different gas properties and flow requirements.
8. Diverse Applications:
Gas flow restrictors find applications in a wide range of industries, including industrial processes, laboratories, gas handling systems,
and environmental monitoring.
Overall, gas flow restrictors play a vital role in ensuring safe, efficient, and controlled gas flow in a wide range of applications. Their ability to provide accurate flow regulation and contribute to the optimization of gas usage makes them indispensable tools in various industrial and scientific processes.
4. How to Install Gas flow Restrictor ?
Installing a gas flow restrictor properly is essential to ensure its effective operation and safe gas flow control.
Here are the general steps to install a gas flow restrictor you can check and follow:
1. Select the Right Type:
Choose a gas flow restrictor that suits your specific application requirements, taking into account factors such as gas type, flow rate, pressure, and temperature.
2. Inspect the Restrictor:
Before installation, carefully inspect the gas flow restrictor for any damage or defects that may have occurred during transportation or handling.
3. Safety Precautions:
Ensure that the gas supply is turned off, and all safety measures are in place before starting the installation.
4. Identify Installation Location:
Determine the appropriate location in the gas system where the flow restrictor needs to be installed. The location should be easily accessible for future maintenance and inspection.
5. Direction of Flow:
Verify the correct orientation of the gas flow restrictor. Some restrictors may have arrows indicating the correct direction of flow, which should be followed during installation.
6. Connect the Restrictor:
Install the gas flow restrictor into the gas line using appropriate fittings or connectors. Ensure a secure and leak-free connection.
7. Verify Compatibility:
Ensure that the chosen flow restrictor is compatible with the gas system's materials and other components.
8. Mounting:
If necessary, securely mount the flow restrictor to a stable surface or structure using suitable brackets or supports.
9. Check Clearances:
Make sure that there is enough clearance around the gas flow restrictor to allow for proper inspection, maintenance, and cleaning.
10. Test the System:
Once the flow restrictor is installed, perform a thorough test of the gas system to ensure that the restrictor is functioning correctly and achieving the desired flow control.
11. Calibration (If Applicable):
If the gas flow restrictor requires calibration, follow the manufacturer's guidelines or calibration procedures to ensure accurate flow rate measurements.
12. Safety Checks:
It's better Double-check that all connections are tight and secure to prevent gas leaks before next step.
13. Marking and Labeling:
Properly mark or label the gas flow restrictor and its installation location for easy identification and reference in the future.
14. Maintenance and Inspection:
Establish a regular maintenance and inspection schedule for the gas flow restrictor to ensure its continued performance and safety.
It is crucial to follow the manufacturer's installation guidelines and any specific instructions provided with the gas flow restrictor to ensure a proper and safe installation. If you are unsure about the installation process or if the gas system is complex, consider seeking assistance from qualified professionals or gas system experts. Remember that safety is of utmost importance when working with gas systems, so always exercise caution and adhere to proper safety protocols during the installation process.
5. Flow Restrictor working principle
The working principle of a flow restrictor is based on creating a pressure drop in the fluid or gas flowing through it. This pressure drop is achieved by introducing a constriction or narrowing in the flow path. As the fluid or gas passes through this narrow passage, its velocity increases, and the pressure decreases.
The Bernoulli's principle and the continuity equation in fluid dynamics explain the working principle of a flow restrictor. According to Bernoulli's principle, an increase in fluid velocity results in a decrease in pressure. The continuity equation states that in an incompressible fluid flow, the mass flow rate remains constant throughout the system.
When a flow restrictor is inserted into a fluid or gas flow path, it creates a restriction or obstruction. As the fluid or gas flows through this restriction, its velocity increases due to reduced cross-sectional area, in accordance with the continuity equation. This higher velocity results in a decrease in pressure, according to Bernoulli's principle.
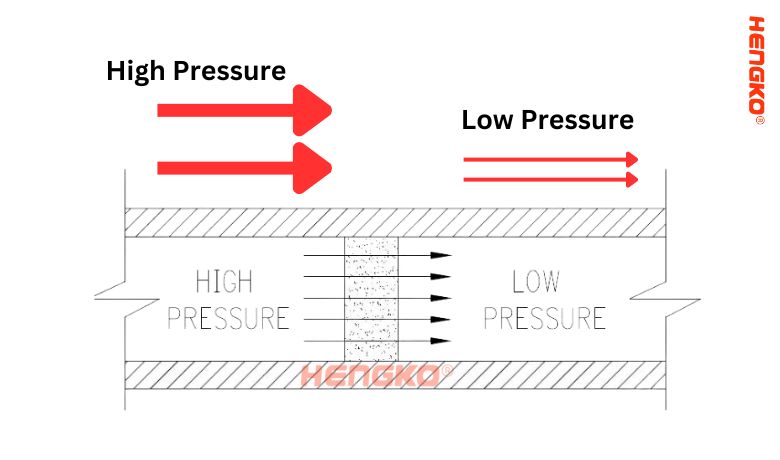
The pressure drop across the flow restrictor helps control the flow rate in the system. By carefully designing the size and geometry of the restrictor, engineers can achieve precise flow control and regulate the flow rate according to specific requirements.
The flow restrictor's working principle allows it to regulate flow rates, maintain safe pressure levels, and control the amount of fluid or gas passing through the system. It is a fundamental component in various industries, from controlling gas flow rates in industrial processes to managing liquid flow in plumbing systems and many other applications that require precise flow control.
6. Which Gas Need to Use Gas Flow Restrictor ?
Gas flow restrictors are used with various types of gases in different applications where flow control is essential. The need to use a gas flow restrictor depends on the specific requirements of the application. Here are some common gases that often require the use of gas flow restrictors:
1. Natural Gas:
Natural gas flow restrictors are commonly used in industrial processes, gas pipelines, and residential applications to regulate gas flow rates and ensure safety.
2. Propane:
Propane gas flow restrictors are utilized in various applications, including propane-powered appliances, heaters, and grills, to control gas flow and optimize fuel consumption.
3. Hydrogen:
Hydrogen gas flow restrictors are used in fuel cells, gas analysis equipment, and hydrogen-based power generation systems to manage gas flow rates accurately.
4. Oxygen:
Oxygen gas flow restrictors are used in medical devices, welding applications, and industrial processes where precise oxygen flow control is necessary.
5. Nitrogen:
Nitrogen gas flow restrictors find applications in various industries, including food packaging, electronics manufacturing, and chemical processes.
6. Argon:
Argon gas flow restrictors are used in welding applications, metal processing, and as shielding gas in various industries.
7. Carbon Dioxide:
Carbon dioxide gas flow restrictors are employed in beverage dispensing, gas analysis equipment, and industrial processes where CO2 flow control is crucial.
8. Chlorine:
Chlorine gas flow restrictors are used in water treatment and disinfection systems, where accurate flow control is essential for safety and effectiveness.
9. Ammonia:
Ammonia gas flow restrictors find applications in refrigeration systems, chemical processing, and industrial cooling applications.
10. Helium:
Helium gas flow restrictors are used in cryogenics, helium leak detection, and scientific research applications.
These are just a few examples, and gas flow restrictors can be used with many other gases depending on the specific industry and application requirements. The primary purpose of using a gas flow restrictor is to achieve precise flow control, maintain safety, optimize gas consumption, and ensure efficient operation in various gas-handling systems and processes.
7. What should you care when Choose A Flow Restrictor for Gas Device ?
When choosing a flow restrictor for a gas device, there are several critical factors to consider to ensure it meets the specific requirements of the application and provides safe and efficient gas flow control. Here are the key considerations:
1. Gas Type:
Determine the type of gas the device will handle, as different gases may have varying properties, such as density, viscosity, and reactivity, which can affect flow behavior and the choice of restrictor.
2. Flow Rate Range:
Understand the required flow rate range for the gas device. Select a flow restrictor that can handle the minimum and maximum flow rates needed for the application.
3. Pressure Conditions:
Consider the operating pressure range of the gas system. Ensure that the chosen flow restrictor can withstand the pressure and maintain accurate flow control.
4. Temperature Range:
Evaluate the temperature range the gas device will operate in. Choose a restrictor that can handle the temperature conditions without compromising performance.
5. Accuracy Requirements:
Determine the level of flow control accuracy needed for the application. Some processes may require precise flow rates, necessitating a more sophisticated flow restrictor.
6. Material Compatibility:
Check the compatibility of the flow restrictor's materials with the gas being used to avoid any chemical reactions or degradation that could affect performance or safety.
7. Device Size and Space Constraints:
Consider the physical dimensions of the flow restrictor and ensure it fits within the gas device or system without causing installation or space issues.
8. Flow Characteristics:
Analyze the flow characteristics required for the application, such as laminar flow or turbulent flow, and select a restrictor that can deliver the desired flow behavior.
9. Pressure Drop:
Evaluate the acceptable pressure drop across the restrictor. A larger pressure drop may lead to energy losses, while too low a pressure drop may not provide sufficient flow control.
10. Application Specifics:
Consider the specific needs of the gas device's application, such as safety requirements, environmental conditions, and regulatory compliance.
11. Customizability:
If needed, check if the flow restrictor can be customized to meet unique application demands, including flow rates, connection types, or materials.
By carefully considering these factors when choosing a flow restrictor for a gas device, you can make an informed decision that best aligns with the specific needs and objectives of the application, ensuring efficient gas flow control and safe operation.
FAQ
1. What are the key features to consider when selecting a gas flow restrictor for a specific application?
When choosing a gas flow restrictor, several critical features should be considered.
Firstly, examine the flow range and accuracy requirements of your application to ensure the restrictor can handle the desired flow rates with precision.
Secondly, assess the pressure and temperature conditions in the gas system, ensuring that the restrictor is compatible with these parameters.
Thirdly, evaluate the flow characteristics needed, such as laminar or turbulent flow, and select a restrictor that matches the desired flow behavior. Material compatibility is another crucial aspect to consider, as the restrictor's materials must be suitable for the specific gas being used to avoid any reactivity or performance issues.
Customizability may be essential in certain applications, so check if the restrictor can be tailored to meet unique demands, such as specialized connection types or flow rate adjustments. Finally, always prioritize reliability and longevity, choosing a high-quality restrictor from a reputable manufacturer to ensure consistent and long-lasting performance.
2. FAQ: How does a gas flow restrictor function in a gas system, and what are its primary roles?
A gas flow restrictor operates by creating a pressure drop in the gas flow, which leads to flow control and regulation.
As the gas passes through the restrictor, its flow is constrained, resulting in a decrease in pressure downstream.
This pressure drop is critical for maintaining controlled gas flow rates and preventing excessive gas release, thereby ensuring safety and efficiency in the gas system. The primary roles of a gas flow restrictor include flow control, pressure regulation, gas conservation, and safeguarding downstream equipment from potential damage caused by high flow velocities.
Additionally, flow restrictors may also be used for gas mixing, dosing, and metering applications, where precise flow rates are necessary for specific processes or experiments.
3. FAQ: What are the key steps involved in installing a gas flow restrictor in a gas system?
Proper installation of a gas flow restrictor is crucial for its effective operation. The key steps include identifying the correct restrictor type and size for the application, inspecting the restrictor for any damage before installation, ensuring safety measures are in place during the process, verifying the direction of flow, securely connecting the restrictor to the gas line with appropriate fittings, and testing the system to ensure the restrictor functions as expected.
It is essential to follow the manufacturer's installation guidelines and any specific instructions provided with the restrictor to ensure a proper and safe installation. If the gas system is complex or the installation process is unfamiliar, consider seeking assistance from qualified professionals or gas system experts.
4. FAQ: What are the typical applications where gas flow restrictors are commonly used?
Gas flow restrictors are widely employed in various industrial, commercial, and scientific applications. You can be found in gas handling systems, gas pipelines, chemical processes, fuel cells, medical devices, environmental monitoring equipment, gas analyzers, gas chromatography, gas-powered appliances, and more. In the oil and gas industry, flow restrictors are used in drilling operations, pipeline flow control, and metering applications. In laboratories, they are integral components of gas analysis equipment, ensuring accurate and consistent gas flow rates for precise measurements.
Additionally, gas flow restrictors find usage in environmental testing and emissions control systems, as well as in gas-powered vehicles and aerospace applications.
5. FAQ: Can a gas flow restrictor be used with different gas types, or does it need to be matched to a specific gas?
The compatibility of a gas flow restrictor with different gas types depends on its design and materials. Some flow restrictors are specifically designed for use with a particular gas due to factors like chemical reactivity, viscosity, or temperature.
However, certain flow restrictors can be used with multiple gas types, especially those made from non-reactive materials, such as stainless steel or inert polymers. When choosing a flow restrictor, it is essential to verify its compatibility with the specific gas being used in the application.
If there is uncertainty about the restrictor's compatibility, consulting the manufacturer or seeking expert advice can help ensure the correct selection.
6. FAQ: What are the advantages of using a gas flow restrictor in gas handling systems?
Gas flow restrictors offer several advantages in gas handling systems.
Firstly, they enable precise control over gas flow rates, allowing for accurate flow regulation and stable operation. This contributes to optimized process efficiency and consistent results in various applications.
Secondly, flow restrictors play a crucial role in ensuring safety by preventing over-pressurization and reducing the risk of gas-related hazards.
Thirdly, they help conserve gas by limiting excessive flow rates, promoting gas savings and reducing operating costs. Additionally, flow restrictors protect downstream equipment from damage caused by high flow velocities, increasing the lifespan and reliability of the system. With their ability to enhance flow control, safety, and gas conservation, gas flow restrictors are essential tools in gas handling systems across a wide range of industries and applications.
For any inquiries or to learn more about our gas flow restrictors and how they can meet your specific application needs, feel free to get in touch with us at HENGKO.
Contact us via email at: ka@hengko.com
Our dedicated team is ready to assist you with product information, technical support, and customized solutions tailored to your gas flow control requirements. We are committed to providing high-quality and reliable gas flow restrictors that ensure safety, efficiency, and precise flow regulation in your gas systems.
Don't hesitate to reach out! We look forward to hearing from you and discussing how our gas flow restrictors can benefit your operations.
Post time: Aug-04-2023