Sensing humidity and temperature is critical, especially in the harsh winters many of us are currently experiencing. It is important not only in daily life, but also in manufacturing industry. For example, when humidity transmitters are properly installed and used, building automation systems can determine when the air becomes too dry or too wet for comfort.
Then how does temperature and humidity sensor work?
First, Temperature Sensor
Temperature sensors are used to determine the amount of heat or cold produced by an object or system. It can sense/detect any physical change in temperature and output analog or digital signals. Temperature sensors fall into two categories: Contact temperature sensors must be in physical contact with the object to be sensed and monitor temperature changes through conduction. Contact temperature sensors monitor temperature changes by convection and radiation.
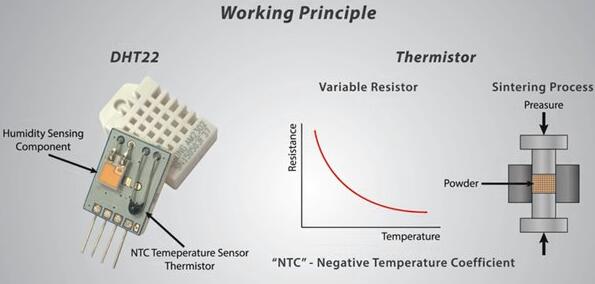
Second, Humidity Sensor
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. The amount of water vapor in the air has an impact on human comfort and various industrial processes. Water vapor also affects a variety of physical, chemical and biological processes. Humidity sensors work by detecting changes in electrical current or air temperature. There are three basic types of humidity sensors: capacitive, resistive and thermal. Each of the three types will continuously monitor small changes in the atmosphere to calculate air humidity.
A capacitive humidity sensor determines relative humidity by sandwiching a thin strip of metal oxide between two electrodes. The electrical capacity of metal oxides varies with the relative humidity of the surrounding atmosphere. The main applications are weather, commercial and industrial. Resistive humidity sensors use ions in salts to measure the electrical impedance of atoms. The electrode resistance on both sides of salt medium changes with humidity. Two heat sensors conduct electricity based on the humidity of the surrounding air. One sensor is sealed in dry nitrogen, while the other is exposed to ambient air. The difference between these two values indicates relative humidity.
A humidity sensor is an electronic device that detects humidity in the environment and converts it into an electrical signal. Humidity sensors come in a variety of sizes and configurations; Some are integrated into handheld devices, such as smartphones, while others are integrated into larger embedded systems, such as air quality monitoring systems. For example, Hengko temperature and humidity transmitters are widely used inthe meteorological, medical, automotive and HVAC industries and manufacturing industries. Industrial grade high precision humidity sensor can ensure accurate measurement in all kinds of harsh environment.
Third, Calculation Method
Humidity sensors are classified into relative humidity (RH) sensors and absolute humidity (AH) sensors according to the method used to calculate the humidity. Relative humidity values are determined by comparing a real-time humidity reading at a given temperature with the maximum humidity in the air at that temperature. Therefore, the relative humidity sensor must measure the temperature to calculate the relative humidity. Absolute humidity, by contrast, is determined independently of temperature.
Forth, the Application of Sensors
Temperature sensors have almost unlimited practical applications, as they are also used in a variety of medical products, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) devices and portable ultrasound scanners. Temperature sensors are used in a variety of appliances in our homes, from refrigerators and freezers to stoves and ovens to ensure they are heated to the right temperature for cooking, air candy/heaters. Even ordinary battery chargers use them to prevent overcharging or undercharging the battery based on its temperature.
While it may seem unlikely that oil extraction will be used for temperature sensors, they are essential to ensure safe and effective oil extraction practices. The oil bit has a temperature sensor at its end that alerts workers when it needs to stop drilling, because when it gets too hot (because it keeps drilling deep into the ground), it can get too hot and break.
The temperature sensor is built into the radiator of the car. This is critical, because when the water circulating through the car engine reaches unsafely high temperatures, they alert you that, if exceeded, could cause engine failure, as well as the car's climate control /. By automatically adjusting parameters according to temperature, this situation is effectively avoided without putting the driver in danger.
HVAC systems require temperature measurements to help maintain the optimum temperature in a room or building. Temperature sensors are needed in almost every air-conditioning unit and system in homes and offices. They can also be used to detect leaks by detecting unexpected temperature anomalies.
Renewable energy relies on temperature sensors to run efficiently. Solar heat pumps, wind turbines, biomass combustion applications and ground heat sources all rely on temperature regulation and measurement.
Fifth, Precision Calibration
To determine the accuracy of the sensor, the obtained values are compared with the reference standard. To verify the accuracy of humidity sensors, we created standards using a "saturated salt" approach. In short, when certain salts (ionic compounds such as table salt or potassium chloride) are dissolved in water, they create an atmosphere of known humidity.
These chemical properties are used to create a microenvironment with a known percentage of relative humidity (RH) (the reference standard), which is then read by a sensor. More precisely, we will prepare the solution in the sealed tank to hold the atmosphere, and then place the connected sensor in the sealed tank. After that, the sensor is read repeatedly and the values are recorded.
We can develop profiles for the sensor under test by repeating this process with several different salts, each of which produces different relative humidity. Because we know the relative humidity of each microenvironment, we can compare the sensor readings with those known values to determine the sensor's accuracy.
If the deviation is large but not insurmountable, we can improve the accuracy of the measurement by using a mathematical calibration procedure in the software.
Also You Can Send Us Email Directly As Follow : ka@hengko.com
We Will Send Back With 24-Hours, Thanks for Your Patient !
Send your message to us:






