As the world's population continues to grow, the demand for food and energy is also increasing. However, traditional agriculture practices are not always sustainable and can be harmful to the environment. To address this issue, a new type of farming known as agrivoltaic farming has emerged, which combines solar power generation with crop production. In this blog, we will explore how agrivoltaic farming works, its benefits and challenges, and its future potential.
What is Agrivoltaic Farming?
Agrivoltaic farming, also known as agrophotovoltaics or APV, is a practice where solar panels are installed above crops to generate electricity while providing shade for the plants. The concept was first developed in the 1980s in Japan, where land is scarce and expensive, and farmers were looking for ways to maximize land use. Agrivoltaic farming has since gained popularity worldwide as a sustainable and efficient way to produce food and energy.
The Agrivoltaic system involves installing solar panels at an appropriate height above the crops to provide shade while allowing enough sunlight to reach the plants. The panels are usually mounted on a framework made of steel or aluminum, and the system is designed to be adjustable to adapt to different crop growth stages. The solar panels are connected to an inverter that converts the DC power produced by the panels into AC power that can be used on the farm or fed into the grid.
Benefits of Agrivoltaic Farming
Agrivoltaic farming offers several benefits, including:
1. Increased crop yields
The shade provided by the solar panels helps to regulate temperature and reduce water loss through evaporation, which can lead to increased crop yields. Studies have shown that agrivoltaic systems can increase crop yields by up to 60% compared to traditional farming methods.
2. Reduced water usage
By reducing water loss through evaporation, agrivoltaic farming can help to conserve water resources. This is particularly important in arid regions where water is scarce.
3. Lower energy costs
By generating their own electricity, farmers can reduce their reliance on the grid and lower their energy costs. In some cases, farmers may even be able to generate excess electricity and sell it back to the grid.
4. Reduced carbon footprint
Agrivoltaic farming reduces greenhouse gas emissions by generating clean, renewable energy and reducing the need for fossil fuels.
5. Diversification of income
By generating both food and electricity, farmers can diversify their income streams and reduce their dependence on a single source of revenue.
Challenges of Agrivoltaic Farming
While agrivoltaic farming offers many benefits, there are also several challenges that must be addressed, including:
1. Initial setup costs
While agrivoltaic farming can provide significant long-term benefits, the initial setup costs can be high. The cost of installing solar panels and other equipment can be a barrier to entry for some farmers, particularly in developing countries.
2. Limited land availability
Agrivoltaic farming requires a certain amount of land to be effective, and in some areas, land may be scarce or too expensive to make agrivoltaic farming economically viable.
3. Technical issues with solar panels
Solar panels require regular maintenance and cleaning to maintain their efficiency. In some cases, weather events such as hailstorms or heavy snow can damage the panels, requiring costly repairs or replacements.
4. Potential conflicts with other land uses
In some cases, agrivoltaic farming may compete with other land uses, such as grazing or forestry. Careful planning and collaboration with other stakeholders is necessary to ensure that agrivoltaic farming does not cause conflicts.
5. Need for specialized knowledge and maintenance
Agrivoltaic farming requires a certain level of technical expertise and maintenance. Farmers need to have knowledge of both agriculture and solar energy systems to operate and maintain agrivoltaic systems effectively.
Future Potential of Agrivoltaic Farming
Despite the challenges, agrivoltaic farming has the potential to play a significant role in sustainable agriculture in the future. The benefits of agrivoltaic farming are clear, and as technology continues to improve and costs decrease, agrivoltaic farming is becoming increasingly accessible to farmers worldwide.
In addition, agrivoltaic farming can be adapted to different crops and regions, making it a versatile solution that can be tailored to local needs and conditions. Agrivoltaic systems can be used to grow a wide range of crops, including vegetables, fruits, and grains, and can be implemented in both rural and urban areas.
Governments and policymakers can also play a significant role in promoting the adoption of agrivoltaic farming. Incentives, subsidies, and support programs can help to lower the costs of installation and maintenance and encourage more farmers to adopt agrivoltaic systems. Policies that promote sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, and carbon sequestration can also create a favorable environment for agrivoltaic farming.

Introducing Temperature and Humidity Transmitter Application for Agrivoltaic Farming
Agrivoltaic farming, also known as agrophotovoltaics, is an innovative approach to sustainable agriculture that combines the generation of solar power with crop production. This innovative system offers numerous benefits, including increased crop yields, reduced water usage, and lower carbon emissions. To ensure optimal crop growth and health, it is essential for farmers to monitor several environmental factors, including temperature and humidity. In this article, we will explore the application of temperature and humidity transmitters in agrivoltaic farming and how they can help farmers to optimize their crop yields.
1. The Importance of Temperature and Humidity Monitoring
Temperature and humidity are two crucial environmental factors that significantly impact crop growth and health. Plants have specific temperature and humidity requirements that must be met to ensure optimal growth and yield. When temperature and humidity levels are too high or too low, crops can suffer from heat stress, drought stress, or disease, leading to reduced yields and lower crop quality.
By monitoring temperature and humidity levels in real-time, farmers can make informed decisions regarding irrigation, ventilation, and other environmental factors to optimize crop growth and yield. However, manual monitoring of temperature and humidity can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, making it difficult for farmers to gather accurate and timely data.
2. The Role of Temperature and Humidity Transmitters in Agrivoltaic Farming
Temperature and humidity transmitters are an essential tool for monitoring environmental conditions in agrivoltaic farming. These devices use advanced sensors to measure temperature and humidity levels in real-time and transmit the data wirelessly to a central monitoring system. This allows farmers to monitor environmental conditions in real-time and make informed decisions regarding irrigation, ventilation, and other environmental factors.
Temperature and humidity transmitters can be installed throughout the agrivoltaic system, providing comprehensive monitoring of environmental conditions. They can be installed in the soil to monitor soil temperature and moisture levels or installed in the air to monitor temperature and humidity levels in the greenhouse or surrounding environment.
3. Benefits of Temperature and Humidity Transmitters in Agrivoltaic Farming
The use of temperature and humidity transmitters in agrivoltaic farming offers several benefits, including:
A: Real-Time Monitoring
Temperature and humidity transmitters provide real-time monitoring of environmental conditions, allowing farmers to make informed decisions regarding irrigation, ventilation, and other environmental factors. This helps to optimize crop growth and yield while reducing water usage and lowering energy costs.
B: Precision Monitoring
Temperature and humidity transmitters use advanced sensors to measure environmental conditions with high accuracy and precision. This ensures that farmers have access to accurate and reliable data that can be used to make informed decisions.
C: Increased Efficiency
The use of temperature and humidity transmitters can increase the efficiency of agrivoltaic systems by reducing the need for manual monitoring and data collection. This saves time and labor costs and allows farmers to focus on other aspects of their operations.
D: Improved Crop Quality
By monitoring temperature and humidity levels, farmers can optimize environmental conditions to promote healthy crop growth and yield. This can lead to higher-quality crops with better flavor, texture, and appearance.
Amazing, there are so many classifications of agriculture. Today, we are learn for the agrivoltaic farming. Agrivoltaics, also known as agrophotovoltaics (APV), is co-developing the same area of land for both solar photovoltaic power as well as for agriculture.
A team of French scientists lead by Christophe Dupraz were the first to use term agrivoltaic. It basically means when solar panels and food crops are combined on the same land to maximize the land use. It’s an idea which could bring food producing to the next level. Their research field in Montpellier, France, indicated that agrivoltaic systems may be indeed very efficient: the increase of global land productivity can be from 35 to 73 percent!
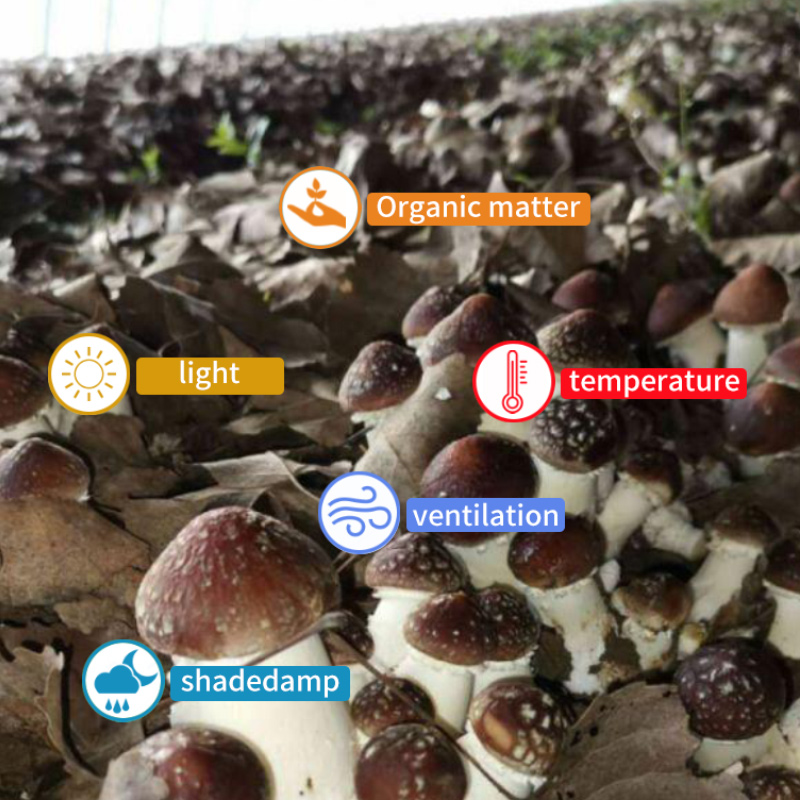
The agrivoltaic greenhouse can meet the power needs of agricultural greenhouses for temperature control, irrigation, and lighting supplement light. And the power generation components on the roof will not occupy the ground, nor will it change the nature of the land, so it can save land resources. It also can meet the lighting needs of different crops, can grow organic agricultural products, precious seedlings, flowers and other high value-added crops, increase the output value per unit of land and the added value of agricultural products, and achieve better economic benefits. Photovoltaic agriculture is widely used in the cultivation of edible fungi. In recent years, with the strong support of national policies, the construction of photovoltaic greenhouses has been promoted in counties across the country, and the “photovoltaic edible fungi industry” model has been adapted to create a “photovoltaic edible fungus” characteristic town.

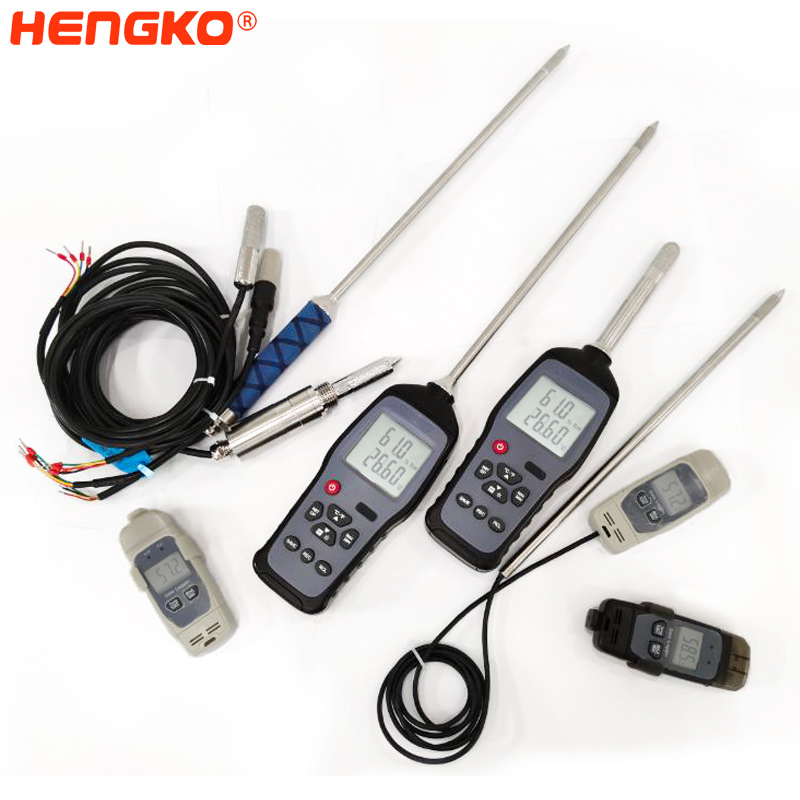
Edible mushrooms are hydrophilic organisms. Regardless of spore germination, hyphae growth, fruit body formation requires a certain amount of moisture and relative air humidity. The water requirement for fruiting bodies of edible fungi during development is very large, and fruiting bodies can only be formed when the substrate has sufficient water content. It can be said that edible fungi that lose their moisture cannot survive. The water of the culture medium is often lost due to evaporation or harvesting, so water is usually sprayed according to the situation. The humidity in the culture medium and the air can be monitored for a long time with a thermometer and hygrometer. The humidity data is mainly to measure the relative humidity. You can use a hygrometer or a temperature and humidity detector that can measure the dry and wet bulb.HENGKO multi-function digital temperature and humidity meter is an industrial, high precision temperature and relative humidity measuring meter. With an external high-precision probe, large LCD for ease of measurement, the data is calculated every 10 milliseconds, and it is sensitive and has the functions of measuring humidity, temperature, dew point temperature, dry and wet bulb data, which can easily meet the needs of accurate temperature and humidity measurement in various occasions.
The following are the requirements of some edible fungi on the moisture and air humidity of the culture medium:
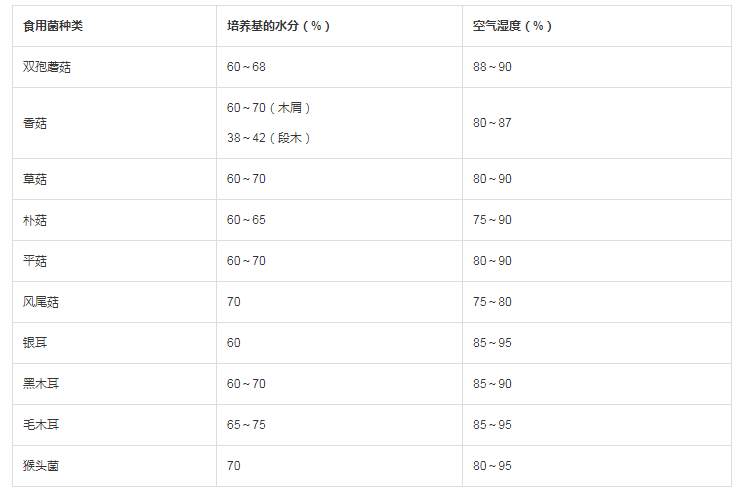
In addition to humidity factors, temperature also plays a very important role in the growth of edible fungi. According to the optimal temperature required for edible fungi mycelium, they can be divided into three categories: low temperature, medium-temperature and high temperature. If the temperature is too high, it will accelerate the evaporation of edible fungi and affect the growth of edible fungi. Since the temperature and humidity factors are so important for the growth of edible fungi, the monitoring of temperature and humidity is the top priority. There are various temperature and humidity sensor series products for you to select. We have professional technology team provides service and customized service of temperature and humidity probe if you have special demand for probe and measuring precision.
Agrivoltaic farming is a new way for rich peasants to reinvigorate agriculture with one light dual purpose and one land dual-use due to technological innovation. China has always strongly supported agricultural poverty alleviation policies, leading farmers on the road to wealth through various poverty alleviation models and promoting agricultural development. We believe agrivoltaic farming will be better in the future!
Conclusion
Temperature and humidity transmitters are an essential tool for monitoring environmental conditions in agrivoltaic farming. They provide real-time, accurate data that can be used to optimize crop growth and yield while reducing water usage and energy costs. By leveraging the power of technology, farmers can create a more sustainable and efficient food system that benefits both farmers and the environment.
Interested in agrivoltaic farming? Know more details about application of the Temperature and Humidity Transmitters in Agrivoltaic Farming,
You are welcome to check our products page or send us enquiry by email ka@hengko.com. we will get back to you within 24-Hours.
Post time: Jun-26-2021







