When you’re responsible for maintaining critical environments — whether in pharmaceutical production,
HVAC systems, electronics manufacturing, or food processing
— you know that moisture control isn’t optional. It’s a core part of ensuring process stability, product quality,
and regulatory compliance.
At this stage, you’re likely evaluating specific solutions to monitor environmental conditions more accurately.
Understanding the difference between dew point, humidity, and air temperature is key to making the right choice.
Here’s why it matters:
1.Dew point and humidity directly impact
product safety, energy efficiency, and operational reliability
2. Excess moisture can lead to condensation, corrosion, microbial growth, or system malfunctions
3. Accurate measurement tools, like dew point and humidity transmitters, help you detect early changes
and respond before issues arise.
Tools that measure dew point are crucial for accurate moisture content assessment, providing better
insights than relative humidity alone. *Different applications may call for
dew point sensors, relative humidity sensors, or a combination of both
By choosing the right type of sensor, you gain:
Tighter control over production environments Improved compliance with industry
standards and audits *Reduced downtime caused by environmental fluctuations
*Better long-term cost efficiency through predictive monitoring
This article will guide you through the core differences between dew point and humidity,
show you how to interpret charts and use calculators, and help you decide which sensor
best fits your specific application.
Dew Point vs Relative Humidity Chart
When you’re selecting a sensor or monitoring system, it’s important to understand
how dew point, temperature, and relative humidity (RH) are connected.
This relationship helps you determine the right measurement method for your application
and ensures you’re choosing a device that provides the data you actually need.
Dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation.
How Dew Point and Relative Humidity Are Related
Relative Humidity (RH)* is the percentage of moisture in the air relative to how much
it can hold at a given temperature
1. Dew Point is the actual temperature at which air becomes saturated and condensation begins
2.As temperature decreases, the air holds less moisture, increasing RH — even if the moisture
content stays the same.
As air temperature drops, the ability of the air to hold moisture decreases, leading to condensation
and the formation of dew when it reaches the dew point. When air cools and reaches its dew point,
fog forms as it can no longer hold all of the moisture, leading to the condensation of water vapor
in the atmosphere.
3.Dew point depends on the humidity levels in the air and stays constant unless moisture is added
or removed from the air
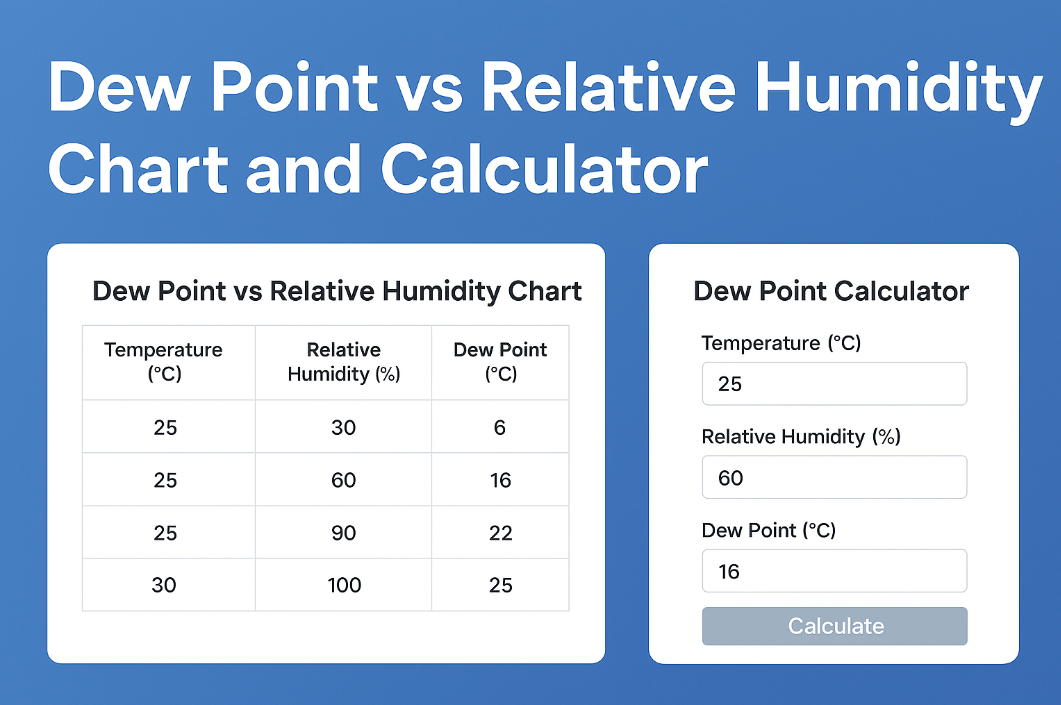
Example Chart Overview
|
Temperature (°C) |
Relative Humidity (%) |
Dew Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
|
25 |
30 |
6 |
|
25 |
60 |
16 |
|
25 |
90 |
22 |
|
25 |
100 |
25 |
As RH increases at a constant temperature, dew point rises When RH hits 100%,
the dew point equals the ambient temperature — this is when condensation forms.
Higher dew points indicate increased humidity and discomfort.
How to Read and Use the Chart
Start with your measured RH and ambient temperature
Use the chart (or a dew point calculator) to find the dew point value
*This is especially useful when you're monitoring environments where condensation control,
drying processes, or moisture-sensitive production is critical
Practical Applications in Industry
You’ll use this chart to:
Predict condensation risk in cleanrooms, cold storage, or electronics manufacturing
Control drying processes in pharma, food, or chemical production
*Ensure safe humidity levels in HVAC and air handling systems
*Optimize compressed air systems by monitoring dew point thresholds
By integrating dew point and humidity sensors with real-time chart-based interpretation,
you can make data-driven adjustments that improve efficiency and avoid costly errors.
Dew Point vs Humidity Calculator
When you’re dealing with precise environmental requirements, sometimes it’s not enough to
rely on manual charts. That’s where dew point and humidity calculators become essential tools
— especially when you need real-time data or quick conversions in the field. The humidity dew point
is a more accurate indicator of moisture content compared to relative humidity, providing clearer
insights into comfort levels and weather conditions.
What Is a Dew Point vs Humidity Calculator?
A dew point calculator helps you determine the dew point temperature based on inputs like:
1.Ambient temperature (°C or °F)
2.Relative humidity (%)
3.Atmospheric pressure (optional, for advanced calculations)
Additionally, hygrometers and air quality monitors are commonly used to measure dew point accurately,
providing valuable data for comfort levels and weather predictions.
When air cools below the dew point, moisture condenses into dew.
It’s used by professionals in:
*Pharmaceutical and biotech labs
*Food and beverage processing
*HVAC maintenance
*Compressed air and gas monitoring
There are many online calculators available, but for real-time accuracy,
built-in sensors and transmitters are far more reliable and efficient.
Real-Time Monitoring with HENGKO Sensors
HENGKO’s industrial-grade sensors and transmitters are designed for accurate and
continuous dew point and RH monitoring, without the need for manual calculations.
With our transmitters, you can:
- *Automatically measure dew point, relative humidity, and temperature
- *View real-time data via digital display, PLC system, or remote dashboard
- *Get fast response times and stable readings in harsh or high-humidity environments
- *Integrate the sensor into your process control system for automated adjustments
This is especially valuable when tight humidity control is required — for example,
in cleanroom operations, storage facilities, or drying chambers.
Sample Calculation Example
Let’s say your production environment is at:
- *Temperature*: 30°C* Relative Humidity: 50 Using a dew point calculator or a HENGKO sensor, you can determine:
- *Dew Point ≈ 18.4°C
This means if the temperature drops to 18.4°C, condensation will begin.
As the air temperature drops, the ability of the air to hold moisture decreases, leading to condensation.
— which could lead to moisture damage if not controlled.
By monitoring this with a real-time sensor, you can proactively adjust ventilation,
cooling, or drying systems to stay within safe limits.
Dew Point vs Moisture Content
As you evaluate measurement solutions, it’s important to recognize that dew point
and moisture content are not the same — even though both deal with water in the
air or in materials.
Dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with moisture, and water vapor
begins to condense. This process of condensation changes vapor into droplets of water, forming
a distinct liquid form. Understanding their difference helps you choose the right sensor for your process.
What Is Moisture Content?
*Moisture content refers to the amount of water present in a solid, liquid, or gas.
A higher dew point indicates a higher absolute amount of water vapor in the air.
*It’s often expressed as a percentage (%) by weight or volume, especially in materials like powders, grains, polymers, or air samples
*Commonly used in industries like:
*Food drying
*Pharmaceutical granulation
*Material processing
*Plastics and packaging
What Is Dew Point?
*Dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with moisture, and water vapor begins to condense
*It is an absolute measurement of moisture in the air — independent of temperature
*Dew point is critical in:
*Compressed air systems
*Cleanrooms
*Drying chambers
*HVAC and climate control
Key Differences
|
Factor |
Dew Point |
Moisture Content |
|---|---|---|
|
What it measures |
Temperature at which condensation starts |
Amount of water in a material or gas |
|
Unit |
°C / °F |
% (by weight or volume) |
|
Application medium |
Air / gas |
Solids, liquids, or air |
|
Sensor type |
Dew point transmitter |
Moisture analyzer or probe |
|
Affected by temp? |
No |
Yes |
When Should You Measure Each One?
Use dew point sensors when:
*You need to prevent condensation
*You're monitoring clean air, gases, or enclosed chambers
*Your process depends on stable, dry environments (e.g. compressed air or electronics)
Use moisture content analyzers when:
*You’re drying materials like grains, powders, or plastics
*You need to control product consistency or shelf life
*Your QC process requires exact moisture balance in solids
Tip for Buyers
If you're monitoring air quality or gas conditions, dew point sensors are your best choice.
For materials or bulk solids, you’ll need moisture content sensors instead.
If you’re unsure, choose a supplier that offers both — or hybrid systems — with support for custom configurations.
Humidity vs Dew Point – Similarities and Differences
If you’re comparing sensor options or trying to decide which parameter is more relevant to your environment,
it’s essential to understand both the similarities and key differences between humidity and dew point.
They’re related — but they give you very different insights. A lower dew point indicates drier air compared to air with a higher dew point.
How Humidity and Dew Point Are Similar
Both measurements help you assess moisture levels in the air, and both are critical for:
*Environmental monitoring
*Quality control
*Preventing condensation, corrosion, and microbial growth
*Ensuring comfort and compliance in controlled spaces
In most cases, dew point and humidity are used together to get a full picture of your environment
— especially in industries like HVAC, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
Key Differences at a Glance
|
Feature |
Relative Humidity (RH) |
Dew Point |
|---|---|---|
|
Definition |
The % of water vapor in the air vs max capacity |
The temp at which air becomes saturated |
|
Unit |
Percentage (%) |
Temperature (°C or °F) |
|
Affected by Temp? |
Yes – RH changes as temperature changes. As air temperature rises or dew point falls, the relative humidity decreases. |
No – dew point remains fixed unless moisture changes |
|
Absolute or Relative |
Relative |
Absolute |
|
Use Case |
Comfort, ventilation, indoor air quality |
Predicting condensation, dryness, and safety |
|
Sensor Type |
RH sensor / humidity transmitter |
Dew point sensor / hygrometer |
Which One Should You Use?
Use Relative Humidity (RH) when:
*You’re managing indoor comfort or ventilation (HVAC)
*You need to maintain general environmental control in workspaces
*Temperature varies and you need real-time % moisture readings
Use Dew Point when:
*You want a fixed value to monitor moisture regardless of temperature
*You need to prevent condensation on surfaces or inside sealed systems
*You're working with compressed air, drying processes, or low humidity environments
Pro Tip
Many modern sensors — like those from HENGKO — measure both dew point and relative humidity in one device.
This gives you a complete picture and allows for smarter process automation, especially in sensitive or high-risk environments.
Industrial Applications of Dew Point and Humidity Sensors
When it comes to choosing the right environmental monitoring solution, context is everything.
Different industries face different risks and compliance challenges — and that’s why understanding
how dew point and humidity sensors are applied in the real world can help you make a confident buying decision.
Below are some of the most common and critical use cases where these sensors make a measurable impact:
1. Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Manufacturing
*Why it matters: Strict regulatory requirements (e.g., GMP, FDA) demand tight humidity control to
ensure product stability and prevent microbial growth.
*Use sensors to:
*Monitor cleanrooms and production lines
*Ensure accurate drying and coating processes
*Protect APIs and formulations from moisture degradation
2. HVAC and Building Automation Systems
*Why it matters: Temperature and RH control directly affect occupant comfort, energy efficiency, and indoor air quality.
*Use sensors to:
*Automate ventilation and dehumidification
*Prevent mold and condensation in ducts and chilled water pipes
*Balance energy use with environmental control
3. Electronics and Semiconductor Facilities
*Why it matters: High humidity leads to static discharge, oxidation, and damage to sensitive components.
*Use sensors to:
*Maintain low dew point in dry rooms
*Protect wafers, PCBs, and precision instruments
*Monitor ESD-sensitive storage and assembly areas
4. Food Processing and Cold Storage
*Why it matters: Moisture causes spoilage, condensation, and inconsistent drying or packaging.
*Use sensors to:
*Optimize humidity during curing, drying, and storage
*Prevent frost buildup in cold chain logistics
*Extend shelf life and maintain hygiene standards
5. Compressed Air and Gas Systems
*Why it matters: Water vapor in compressed air can corrode pipelines, damage tools, and affect pneumatic performance.
*Use sensors to:
*Monitor dew point in dryers and compressors
*Detect leaks and ensure ISO 8573 compliance
*Automate maintenance scheduling based on real-time conditions
6. Industrial Coating, Printing, and Material Processing
*Why it matters: Surface moisture and environmental humidity can affect adhesion, finish quality, and drying rates.
*Use sensors to:
*Control humidity in paint booths and curing ovens
*Maintain consistency in plastics, textiles, and composites
*Avoid costly rework due to moisture-related defects
Bonus: Environmental and Climate Research
*Use sensors to:
*Monitor air quality, greenhouse conditions, and meteorological data
*Support sustainability and energy optimization projects
*Improve climate control in greenhouses or labs
Choosing the Right Sensor or Transmitter Step by Step
Now that you understand the differences between dew point and humidity — and how they
apply across industries — the next step is choosing the right type of sensor or transmitter
for your environment.
Choosing correctly means fewer process disruptions, better compliance, and long-term cost savings.
Here's how to make the best choice for your application:
Step 1: Identify What You Need to Measure
Ask yourself:
*Are you primarily concerned with condensation risks, dry air, or gas system monitoring?
→ You need a dew point sensor
*Are you focused on general room climate, ventilation, or comfort/hygiene control?
→ You need a relative humidity (RH) sensor
*Do you need both? Many applications benefit from dual-output sensors for complete environmental control
Step 2: Match the Sensor to the Application Environment
Consider the operating conditions:
*High temperature or high humidity zones (e.g., drying ovens, tropical climates)
→ *Choose sensors with high-temperature tolerance and fast recovery time
*Cleanrooms, HVAC ducts, or industrial enclosures
→ *Look for compact designs, fast response time, and digital output options
*Outdoor or harsh environments
→ *Choose rugged sensors with IP65 or IP67 housing and corrosion-resistant construction
Step 3: Look for Key Features That Fit Your Process
*Accuracy: ±1.5% RH or better; ±1°C dew point accuracy is ideal for precision applications
*Output type: 4–20mA, RS485, Modbus, or digital display depending on your system
*Response time: Faster response = better real-time control
*Calibration: Choose pre-calibrated sensors or ones with field calibration options
*Mounting & Integration: Wall-mounted, duct-mounted, or probe-style — depending on your setup
Why Choose HENGKO?
HENGKO offers a wide range of industrial-grade dew point and humidity transmitters, designed to meet the demands of:
*Cleanrooms and pharmaceutical manufacturing
*HVAC systems and air quality monitoring
*Compressed air and gas systems
*Food, beverage, and chemical processing environments
We also provide:
*OEM and custom solutions tailored to your project
*Rugged, stainless steel housing for harsh conditions
*Dual-sensor models combining dew point, RH, and temperature in one unit
*Fast delivery and technical support for global customers

Not Sure What to Choose?
If you're unsure whether to monitor dew point, humidity, or both — or which sensor fits your process
— our team can help. We'll walk you through the best-fit options based on your environment, industry,
and technical requirements.
Conclusion
When it comes to maintaining control over environmental conditions, understanding the relationship
between dew point and humidity is more than just theory — it’s a practical necessity.
Whether you're working in pharma, HVAC, electronics, food processing, or compressed air systems,
the right monitoring approach can protect your products, reduce downtime, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Here’s what you should remember:
*Humidity tells you how saturated the air is
*Dew point tells you the exact temperature at which condensation begins
*Each metric plays a critical role, depending on your environment and goals
*The right sensor or transmitter makes all the difference in accuracy, stability, and reliability
By selecting high-performance instruments — like the industrial-grade sensors and transmitters from HENGKO
— you’re investing in long-term control, quality assurance, and peace of mind.
Ready to Choose the Right Sensor?
1.Need help with sensor selection?
Our technical team can recommend the best-fit model for your application.
2.Looking for custom or OEM options?
We provide tailored solutions to meet your exact project requirements.
3.Want to get a quote or place a bulk order?
Contact us today for pricing, specifications, and delivery timelines.
Get in Touch Now
Contact HENGKO Sales Team Today !
Visit our website: www.hengko.com
Email: sales@hengko.com
Let us help you monitor with confidence
— from dew point to humidity, from lab to factory floor.
Post time: Apr-02-2025




