Why Dew Point Instrument Measuring Air Trace Moisture Content is so important.
Dew point temperature needs to be focused on in many industrial control environments. At any temperature, the maximum amount of water vapor that the air can hold is called the water vapor saturation pressure. At this time, adding more water vapor will cause condensation. Condensation is less desirable in compressed air systems, as it can lead to clogged pipes, machine failures, contamination, and freezing.
What effect does pressure have on the dew point? Air compression with an air compressor increases the water vapor pressure and thus the dew point value. Therefore, the fixed-point dew point value measured by the dew point meter will be different from the dew point value in the compressed air process.
What is the Typical Range of Dew Point?
Normally, We Care The typical range of dew point refers to the span of dew point temperatures commonly encountered in various atmospheric conditions. The dew point temperature represents the temperature at which the air becomes saturated with moisture, leading to condensation and the formation of dew or fog. The range can vary depending on the climate, location, and prevailing weather conditions.
In general, the typical range of dew point temperatures can vary from below freezing (-40°C or lower) in extremely dry or cold climates to high temperatures above 25°C in tropical and humid regions. Here is a breakdown of the typical range of dew point temperatures:
-
Dry Climates: In arid and desert regions, where the air is typically very dry, the dew point temperature tends to be extremely low. The dew point can range from -40°C to 0°C or slightly above, indicating minimal moisture content in the air.
-
Moderate Climates: In temperate regions with moderate humidity levels, the range of dew point temperatures generally falls between 0°C and 20°C. This range is commonly encountered in many parts of the world, including regions with four distinct seasons.
-
Humid Climates: In tropical and humid regions, where moisture content in the air is high, the dew point temperature can reach and exceed 25°C. These areas experience consistently high humidity, resulting in a higher dew point range.
It is important to note that these ranges are general guidelines and can vary depending on local climate patterns, geographic location, and prevailing weather conditions. Furthermore, the range of dew point temperatures can fluctuate significantly within a single day or over different seasons, influenced by factors such as air temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure.
Dew point is a crucial parameter for assessing atmospheric moisture levels, managing humidity, and predicting weather conditions. Understanding the typical range of dew point temperatures helps in interpreting and analyzing meteorological data, as well as making informed decisions related to activities that are sensitive to moisture, such as agriculture, outdoor events, and construction projects.
How to Measuring the Inter Air Dew Point of System?
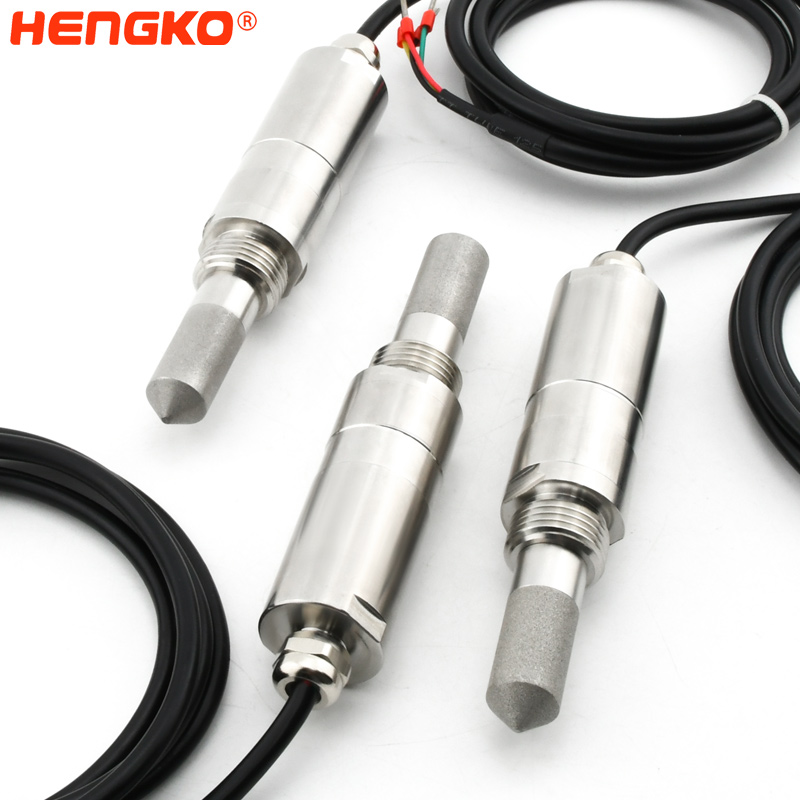
We need to choose a dew point transmitter or dryer dew point meter with a suitable measuring range. HENGKO HT608 series dew point meter suitable for high pressure system operation, some dew point meters on the market can’t withstand high pressure, or imported meters are too expensive. 608 series dew point sensor transmitter not only can withstand high pressure but can output temperature and humidity, dew point temperature, wet bulb temperature, high precision, good consistency.
What instrument is used to measure dew point ?
HENGKO's 608 dew point transmitter is installed to measure the compressed air after expansion to atmospheric pressure, but if the pressure dew point is the required measurement parameter, the measured dew point value must be corrected.
The installation needs to follow the manufacturer's instructions, especially do not install the dew point sensor at the end of a short pipe without air flow or other "dead corner" pipes. If you install the measurement in these places, not only the measurement range is small, but another problem is that the measurement is inaccurate and the product itself is easily damaged.
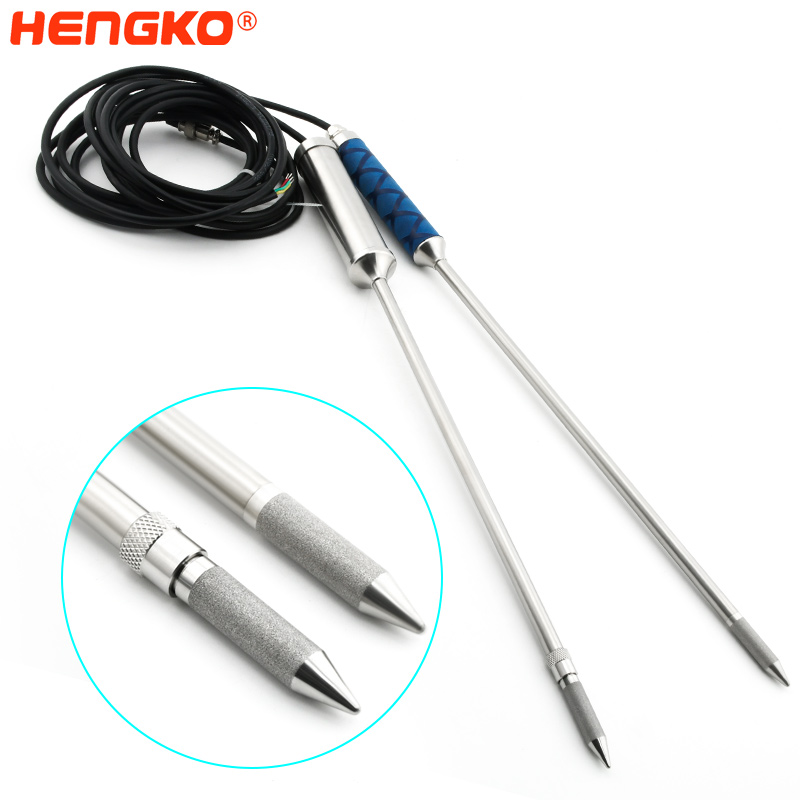
For narrow and long pipes or boxes, 608c or 608d dew point meters are very suitable for measurement, 316L stainless steel extension tube, slim, rigid, low resistance, convenient for measurement in narrow spaces; High accuracy, good repeatability, good long-term stability;
There are two types of probes: pluggable and non-pluggable, which are convenient to apply to different environmental scenarios, meet your different needs, and extend the service life of the instrument.
Application of Dew Point Measuring Instrument
Dew point measuring instrument is widely used in dryers, compressed air systems, air separation, petrochemical, metallurgy, electronic power, machinery manufacturing and other industries. A lot of industrial products need to be evaluated and monitored for trace water content, such as high purity gas has strict requirements for water, because the water of the gas can not only dissolve some gas components but also produce acid or alkali with some components in a chemical reaction, corrosion equipment or instrument damage.
1. Industrial Processes and Manufacturing:
Dew point measurement plays a vital role in industrial processes, especially those involving sensitive materials or equipment. It helps prevent condensation and corrosion, ensuring product quality and equipment longevity. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, chemicals, and electronics rely on dew point measuring instruments to maintain optimal humidity levels during manufacturing, storage, and transportation.
For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, dew point instruments are utilized to monitor and control the humidity inside cleanrooms and production facilities. This ensures that drugs and medical devices remain stable, preventing moisture-induced degradation and preserving their efficacy.
2. HVAC and Building Management Systems:
Dew point measurement is essential for maintaining comfortable and healthy indoor environments in buildings. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems utilize dew point measuring instruments to control humidity levels, prevent condensation, and minimize the growth of mold and bacteria. By continuously monitoring the dew point, HVAC systems can adjust temperature and humidity settings to ensure optimal conditions for occupant comfort and energy efficiency.
Building management systems (BMS) also employ dew point measurement to optimize energy consumption and reduce the risk of moisture-related damage to building structures, such as walls, ceilings, and insulation. By integrating dew point sensors into BMS, facility managers can take proactive measures to prevent costly repairs and maintain a safe and sustainable environment.
3. Compressed Air and Gas Systems:
In industries where compressed air and gases are utilized, dew point measuring instruments are crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of these mediums. Compressed air systems can generate moisture due to air compression, and if left unchecked, this moisture can cause corrosion, equipment malfunction, and product contamination. By accurately measuring the dew point, operators can implement appropriate drying and filtration systems to remove excess moisture, protecting equipment and product integrity.
Dew point measurement is also critical for monitoring and maintaining the purity of gases used in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, laboratory research, and medical applications. Certain gases, such as high-purity nitrogen or oxygen, need to be free from moisture to prevent reactions or contamination. Dew point measuring instruments enable real-time monitoring and control of moisture levels in gas systems, ensuring optimal gas quality and performance.
4. Power Generation and Electrical Equipment:
Moisture control is essential in power generation processes and electrical equipment to maintain operational efficiency and prevent electrical failures. High humidity levels can lead to insulation degradation, electrical arcing, and equipment malfunction. Dew point measuring instruments provide accurate and continuous monitoring of humidity levels in transformers, switchgear, and other electrical systems, enabling preventive maintenance and reducing the risk of costly downtime.
Power plants, including thermal and nuclear facilities, rely on dew point measurement to optimize combustion processes, prevent corrosion in turbine systems, and maintain the performance of cooling towers. By monitoring and controlling the dew point, operators can enhance energy efficiency, extend the lifespan of equipment, and minimize environmental impacts.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of dew point measuring instruments. From industrial processes to building management and power generation, these instruments play a crucial role in maintaining optimal humidity levels, preventing moisture-related damage, and ensuring product quality and operational efficiency across various industries.
How to Measure Dew Point with What Instrument
The dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with moisture, causing water vapor to condense into liquid water (dew). Measuring the dew point is important in various industries, particularly meteorology and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning).
The instrument used to measure dew point is called a dew point meter or hygrometer. There are different types of dew point meters, each working on a different principle. Here are some common methods and their respective instruments:
1. Chilled Mirror Hygrometer:
This is one of the most precise methods to measure the dew point. The instrument cools a mirror until condensation forms on it. The temperature at which this condensation occurs is the dew point. A sensor then measures the temperature of the mirror, giving a direct measurement of the dew point.
2. Capacitive Hygrometers:
These devices have a moisture-sensitive capacitor. The dielectric constant of this capacitor will change with the amount of moisture absorbed. By measuring the capacitance, the relative humidity can be determined, which can then be used to find the dew point.
3. Resistive Hygrometers:
These contain a humidity-sensitive material (often a type of salt or conductive polymer). As the material absorbs or releases moisture, its electrical resistance changes. By measuring this resistance, relative humidity can be inferred and then converted to a dew point.
4. Hair Hygrometer:
This older style of hygrometer uses human or animal hair under tension. The hair length changes with humidity, and these changes can be used to estimate the relative humidity and subsequently the dew point. However, it is less accurate than other modern methods.
5. Absorption Hygrometers:
These use a material (like lithium chloride) that will absorb moisture. The change in weight of the material can be used to infer the relative humidity, which can then be converted to dew point.
6. Electronic Dew Point Meters:
Modern digital meters can often combine several of the above principles (especially capacitive and resistive) to measure dew point directly or calculate it from relative humidity.
To get an accurate dew point reading:
1.) Make sure the instrument is calibrated and properly maintained.
2.) Consider the specific application and choose the appropriate instrument accordingly. For example, chilled mirror hygrometers are excellent for laboratory settings, but may not be ideal for rough field conditions.
Once you've measured the dew point, it can be used in various calculations and assessments, from predicting fog or frost to ensuring that industrial processes are occurring under the right conditions.
Why compressed air need to use dew point transmitter ?
A dew point transmitter is used in compressed air systems for several important reasons:
1. Moisture Control:
Compressed air can contain moisture in the form of water vapor. When the air cools down, such as when it travels through pipelines or is used in various applications, this moisture can condense into liquid water. Excessive moisture in compressed air can lead to various issues, including damage to equipment, corrosion, and reduced efficiency in pneumatic tools and processes. A dew point transmitter helps monitor and control the moisture content by measuring the temperature at which condensation (dew) would occur.
2. Preventing Corrosion:
Moisture in compressed air can cause corrosion in pipelines, valves, and other components of the system. This corrosion can lead to leaks, reduced system lifespan, and increased maintenance costs. By maintaining the dew point temperature at an acceptable level, a dew point transmitter helps prevent corrosion-related problems.
3. Quality Assurance:
In some applications, such as in the food and pharmaceutical industries, the quality of compressed air is critical. Moisture in the air can lead to contamination and compromise product quality. Dew point transmitters ensure that the compressed air meets specific quality standards by monitoring and controlling moisture levels.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Removing excess moisture from compressed air can improve its energy efficiency. Wet air requires more energy to compress and transport, so by maintaining a lower dew point temperature, you can reduce energy consumption and operating costs.
5. Equipment Protection:
Moisture can be harmful to various components of compressed air systems, including air compressors, pneumatic tools, and instrumentation. By using a dew point transmitter to manage moisture levels, you can extend the lifespan of your equipment and reduce the need for costly repairs or replacements.
In summary, a dew point transmitter is a crucial tool in compressed air systems to ensure that moisture levels are kept in check. It helps prevent problems related to corrosion, contamination, and energy inefficiency while ensuring the overall reliability and performance of the compressed air system.
FAQs
Q1: What are the key features of a dew point instrument?
A dew point instrument typically comes with several key features that enhance its functionality and usability. These features may include:
a) Sensor Technology:
Dew point instruments employ various sensor technologies, such as capacitive, chilled mirror, or ceramic sensors. These sensors provide accurate and reliable measurements of moisture content in gases or ambient air.
b) Measurement Range:
Dew point instruments offer a wide measurement range to cater to different applications and varying levels of humidity. The range can typically extend from ambient conditions to extremely low dew points, such as -80°C or lower.
c) Display and Interface:
The instrument is equipped with a clear and user-friendly display that shows the measured dew point value, temperature, and other relevant parameters. It may also have an intuitive interface for easy navigation and configuration of settings.
d) Data Logging and Connectivity:
Many dew point instruments have built-in data logging capabilities, allowing users to store and retrieve measurement data for analysis and documentation. Additionally, they may offer connectivity options such as USB, Ethernet, or wireless communication for seamless data transfer and integration with other systems.
e) Alarm and Alert Functions:
Dew point instruments often feature configurable alarms and alerts to notify users when the measured dew point exceeds predefined thresholds. These functions help prevent potential damage or operational issues caused by excessive moisture.
Q2: What are the functions of a dew point instrument?
Dew point instruments serve several essential functions related to moisture measurement and control. These functions include:
a) Dew Point Measurement:
The primary function of a dew point instrument is to accurately measure the dew point temperature, which indicates the point at which moisture in the air or gas will condense. This measurement is crucial for assessing moisture levels, preventing condensation, and maintaining optimal humidity conditions.
b) Moisture Content Analysis:
Dew point instruments enable the analysis of moisture content in gases or ambient air. By quantifying the amount of moisture present, users can assess the suitability of the environment for specific applications, identify potential sources of moisture, and take necessary measures to control humidity.
c) Real-time Monitoring:
Dew point instruments provide real-time monitoring of moisture levels, allowing users to track changes in humidity and respond promptly to deviations from desired conditions. Continuous monitoring ensures proactive control and early detection of moisture-related issues.
d) Process Control:
Dew point instruments are often integrated into control systems to regulate moisture levels in industrial processes. By monitoring the dew point, these instruments enable the implementation of appropriate drying systems, filtration, or ventilation to prevent moisture-related problems, such as corrosion, product degradation, or equipment malfunction.
e) Maintenance and Troubleshooting:
Dew point instruments aid in maintenance activities by identifying areas prone to condensation or excessive moisture accumulation. They assist in troubleshooting by pinpointing potential sources of moisture-related problems, enabling timely repairs and preventive measures.
Q3: How should a dew point instrument be installed?
The installation of a dew point instrument requires careful consideration to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. Here are some general guidelines for installation:
a) Location:
Select an installation location that is representative of the area or process being monitored. Avoid locations with direct exposure to external factors that could impact moisture levels, such as air conditioning vents or heat sources.
b) Mounting:
Mount the instrument securely on a stable surface, preferably using brackets or mounting plates provided by the manufacturer. Ensure that the instrument is properly aligned and positioned for easy access to the display, interface, and sample inlet/outlet.
c) Sample Conditioning:
If the instrument is used for measuring the dew point of gases, ensure proper sample conditioning. This may involve removing particulates, filtering out impurities, and controlling the flow rate and pressure of the gas sample before it reaches the instrument's sensor.
d) Calibration:
Before putting the instrument into operation, perform calibration according to the manufacturer's instructions. Calibration ensures the accuracy and reliability of the measurements.
e) Regular Maintenance:
Establish a maintenance schedule to clean and inspect the instrument periodically. This helps to ensure its continued accuracy and longevity.
It is crucial to consult the instrument's user manual or seek guidance from the manufacturer for specific installation instructions, as they may vary depending on the model and application.
Q4: What are the applications of dew point instruments?
Dew point instruments find applications across various industries and processes where moisture control is critical. Some common applications include:
a) Industrial Processes:
Dew point instruments are used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, chemicals, electronics, and textiles. They aid in maintaining optimal humidity levels during manufacturing, storage, and transportation, ensuring product quality, equipment longevity, and compliance with industry standards.
b) HVAC and Building Management:
Dew point instruments play a vital role in HVAC systems and building management. They help control humidity levels, prevent condensation, and minimize mold growth in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, ensuring occupant comfort and energy efficiency.
c) Compressed Air and Gas Systems:
Dew point instruments are essential for maintaining the quality and reliability of compressed air and gases. They help prevent corrosion, equipment malfunction, and product contamination caused by excessive moisture. These instruments find applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing.
d) Power Generation and Electrical Equipment:
Dew point instruments are utilized in power plants and electrical systems to monitor moisture levels and prevent electrical failures caused by insulation degradation. They aid in optimizing combustion processes, protecting turbine systems, and maintaining the performance of cooling towers.
e) Laboratory and Research:
Dew point instruments are employed in laboratories and research facilities to control and monitor humidity levels. They ensure stable and controlled environmental conditions for experiments, sample storage, and sensitive equipment operation.
These are just a few examples of the broad range of applications where dew point instruments are indispensable for moisture measurement, control, and maintenance. The specific application and requirements will dictate the selection and utilization of the instrument.
Still Have Any Questions for the Dew Point Instrument Measuring Air Trace Moisture Content, You are welcome
to contact us by email ka@hengko.com for products details and price list. We will send back to you with best
introduce for your monitor project.
Post time: Dec-27-2021